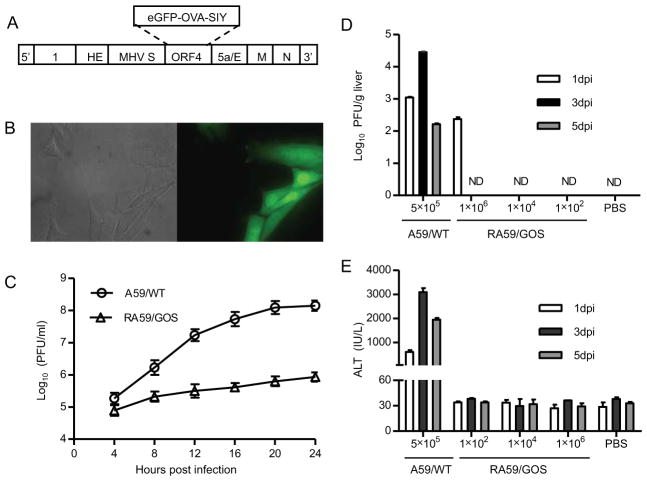
FIGURE 1. Construction and characterization of recombinant MHV-A59 expressing an eGFP-OVA-SIY fusion protein.
(A) Schematic diagram of recombinant MHV virus. Targeted RNA recombination was used to replace ORF4 of MHV-A59 with a sequence encoding eGFP-OVA-SIY fusion protein. The eGFP-OVA-SIY fusion gene was first cloned into pMH54 plasmid via Sal I and Not I sites, and then transcribed into RNA for recombination with feline MHV in AK-D cells. See Materials and Methods for details.
(B) eGFP fluorescence of RA59/GOS infected cells. 17Cl-1 cells were seeded on cover glass in 6-well plate followed by RA59/GOS infection at MOI of 1. Eight hours post infection, cells were fixed and visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Bright field and fluorescent images of the same area are shown.
(C) Comparison of replication of wild-type and recombinant MHV-A59 in cultured cells. 17Cl-1 cells were infected in triplicates with A59/WT or RA59/GOS at MOI of 1. Culture supernatants were harvested every 4 hrs and assayed for virus titer by plaque assay. The mean virus titer ± standard deviation (SD) of triplicate samples is shown. Representative results from one of three experiments are shown.
(D, E) Comparison of virus titers and ALT levels in B6 mice infected with A59/WT or RA59/GOS. B6 mice were inoculated i.p. with A59/WT (5×105 pfu/mouse) or the indicated doses of RA59/GOS. PBS injected mice were used as control. At 1, 3 and 5 dpi, sera and livers were harvested for assaying ALT levels and virus titers, respectively. Virus titers (D) and ALT levels (E) are shown as mean ± SD of 5–6 mice per group. ND, not detectable. Representative results from one of three experiments are shown.