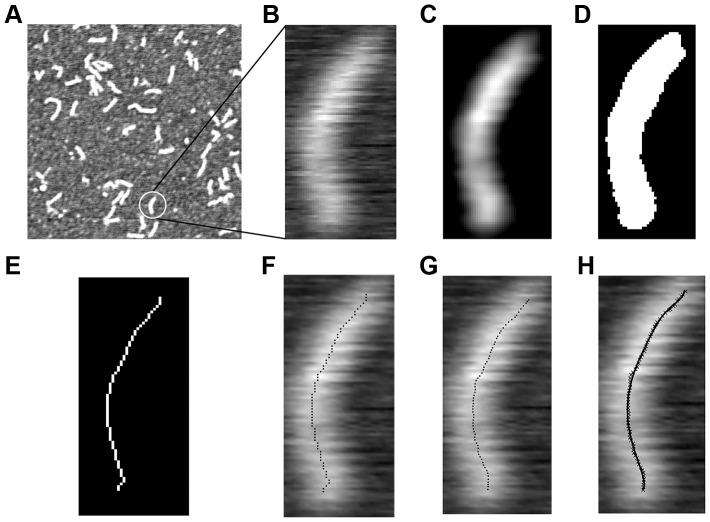
Figure 2. Image processing procedure to extract the molecular contour of αTm from a typical AFM scan.
An αTm molecule was selected from a typical 512 nm ×512 nm scan (A) and cropped into a smaller image (B). The image was filtered by a Gaussian box-car filter (C), thresholded (D), and skeletonized into a 1-pixel wide connected contour (E, F). A refined skeleton with coordinates defined at sub-pixel precision was generated by fitting the perpendicular height profiles to a Gaussian function (G), which was then fitted with a 5th order polynomial. The continuous contour defined by the polynomial conformed very well with the shape of the original molecule (H). Contour length (Lc) and end-to-end length (Le-e) of the molecule shown were 41.7 nm and 38.4 nm, respectively.