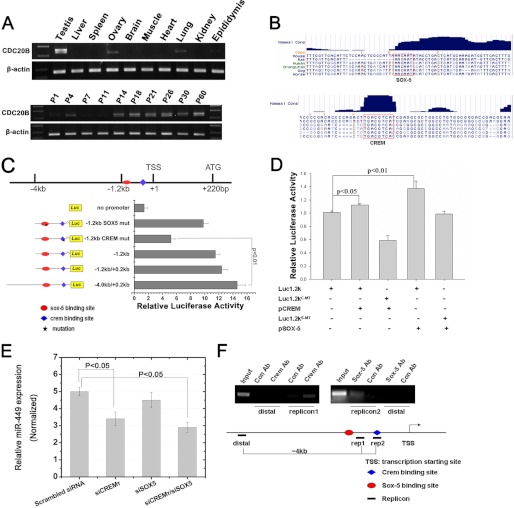
FIGURE 2.
CREMτ and SOX5 transactivate miR-449 expression by binding two conserved cis-elements upstream of Cdc20b. A, RT-PCR analyses of Cdc20b expression in multiple adult mouse tissues (upper panel) and developing mouse testes (lower panel). B, schematic representation of putative conserved CREMτ and SOX5 binding sites (highlighted with red boxes) in the promoter region of Cdc20b. C, mapping of the upstream transcriptional regulatory region of Cdc20b/miR-449 cluster by luciferase reporter assays. Luciferase plasmids containing a partial deletion or mutation in CREMτ and SOX5 binding sites were constructed as indicated. Normalized luciferase activity is represented as mean ± S.E. (n = 3). All groups were performed in triplicate. D, co-transfection luciferase reporter assays using the GC-2 cell line identified that both CREMτ (p < 0.05) and SOX5 (p < 0.01) proteins can efficiently activate the −1.2 kb-containing reporter construct. Various combinations of plasmids transfected into GC-2 cells are indicated below each group. Luc1.2kC-MT, luciferase construct containing a mutation in the candidate CREMτ binding site; Luc1.2kS-MT, luciferase reporter containing a mutation in the candidate SOX5 binding site. E, knockdown of CREMτ individually or knockdown of CREMτ and SOX5 simultaneously using siRNAs led to decreased levels of miR-449 in GC-2 cells (n = 3; p < 0.05). siCREMτ, siRNA designed against CREMτ mRNA; siSOX5, siRNA designed against SOX5. Small nucleolar RNU6B was concurrently amplified for data normalization. F, ChIP assays confirmed the binding of both CREMτ and SOX5 to the −1.2 kb promoter region upstream of Cdc20b gene. rep1, rep2, and distal represent three different PCR fragments designed against the genomic region as indicated. Luc, luciferase; mut, mutant; TSS, transcription start site; Ab, antibody; Con, control. Data are represented as mean ± S.E. (n = 3).