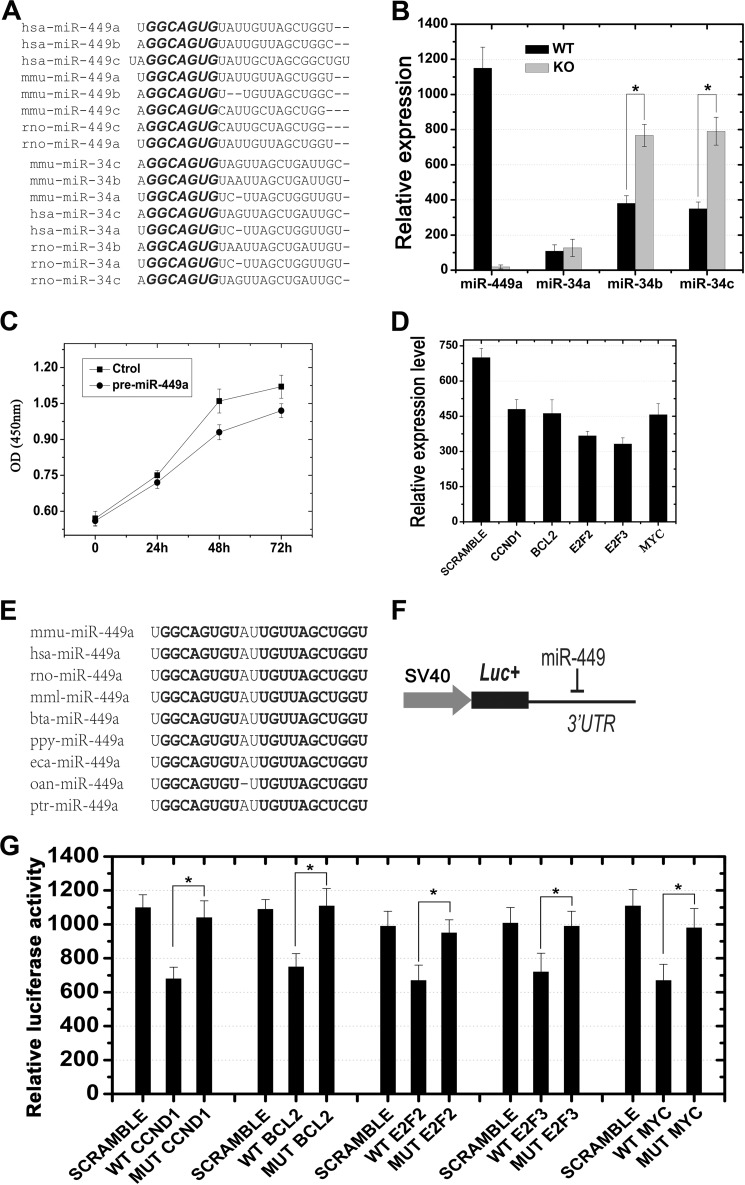
FIGURE 4.
Shared mRNA targets between miR-449 and miR-34b/c and potential compensatory effects of miR-34b/c in miR-449 knock-out mice. A, high similarity of mature sequences between members of the miR-449 cluster and the miR-34 family from humans, mice, and rats. The conserved motif “GGCAGUG” located in the “seed region” of each miRNA is highlighted in bold. B, qPCR analyses showing that levels of miR-34b and miR-34c, rather than miR-34a, were notably up-regulated in miR-449 KO mice as compared with those in wild type. *, p < 0.05. C, cell proliferation assays showing a time-dependent decrease in total cell number of GC-1 cells transfected with pre-miR-449a compared with the scrambled transfection control (Ctrol). D, qPCR analysis of levels of mRNAs for CCND1, BCL2, E2F2, E2F3, and MYC in HeLa cells transfected with pre-miR-449a. The values were normalized against GAPDH endogenous control. E, highly conserved miR-449a sequences among nine species. Sequences highlighted in bold indicate identical nucleotides. F, schematic illustration of the luciferase reporter assay. The 3′-UTR sequence for each target gene was inserted downstream of the luciferase coding sequence in pGL3.0 control vector (Promega) as described previously (19). G, luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that miR-449 was capable of repressing expression of genes encoding factors belonging to the E2F-pRb pathway, including CCND1, BCL2, E2F2, E2F3, and MYC (n = 3; *, p < 0.05). SCRAMBLE, a non-sense double strand siRNA showing no homology to any mRNA in the murine genome. Data are represented as mean ± S.E. (n = 3).