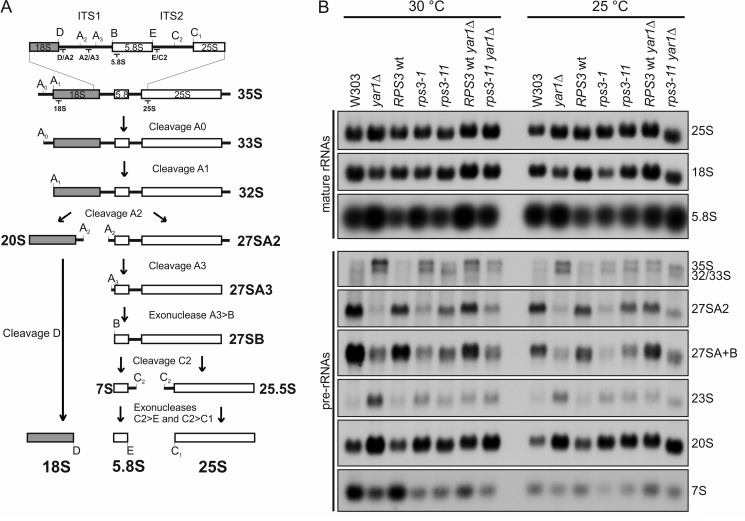
FIGURE 5.
yar1 and rps3 mutants accumulate 20S pre-rRNA. A, simplified rRNA processing pathway in yeast. Only the major pathway for generation of the 5′-end of the 5.8S rRNA is shown. The rRNA cleavage sites and the binding sites of the probes used for Northern blotting are indicated. ITS1 and 2: Internal transcribed spacers 1 and 2. In the course of pre-rRNA processing, the 35S pre-rRNA undergoes a series of endonucleolytic processing events at sites A0, A1, and A2 that lead to the separation of the 20S and 27SA2 pre-rRNAs. Endo- and exonucleolytic processing steps of the 27SA2 pre-rRNA finally yield the mature 25S and 5.8S rRNAs contained in 60S subunits. In the cytoplasm, the final processing step in 40S maturation takes place when the 20S pre-rRNA is converted into the 18S rRNA by endonucleolytic cleavage at processing site D. The aberrant 23S RNA, which is generated by premature cleavage of the 35S pre-rRNA at site A3 is not shown. B, steady-state levels of pre-rRNA and mature rRNA in yar1 and rps3 mutants. Cells were grown at 25 °C or 30 °C to an A600 of 0.6. RNA was isolated, separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, and transferred to a nylon membrane. Pre-rRNA processing intermediates were detected by Northern blotting using the following probes: “A2/A3” for detection of 35S, 33S/32S, 27SA2, and 23S RNAs, “E/C2” for detection of 27SA+B (27SA2, 27SA3 and 27SB) and 7S pre-rRNAs, “D/A2” for detection of the 20S pre-rRNA. Sequences of the probes are given in “Experimental Procedures”; binding sites of the probes are indicated in A.