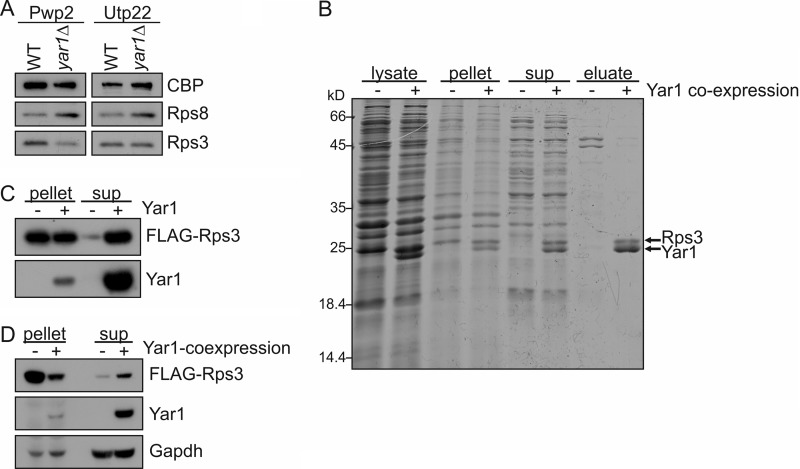
FIGURE 7.
Yar1 keeps Rps3 soluble. A, 90S particles from a yar1Δ strain contain less Rps3. Pwp2-TAP and Utp22-TAP were purified from yeast cells. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using anti-CBP, anti Rps8 and anti-Rps3 antibodies. Note that in both purifications, Rps3 levels are reduced when compared with Rps8, which was used as a loading control for pre-ribosomal particles. B, Rps3 expressed in E. coli is only soluble upon co-expression of Yar1. Rps3 was either expressed alone as a His6 tag fusion (−) or co-expressed as a FLAG tag fusion with His6-Yar1 (+) in E. coli. Cells were lysed by sonication and lysates were centrifuged at 40,000 × g to pellet insoluble material. The supernatant was used for affinity purification of His6-Rps3 and His6-Yar1. Samples from the lysate, the 40,000 × g pellet, the 40,000 × g supernatant (sup), and the eluate from the affinity purification were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. C, Yar1 protects purified Rps3 from precipitation. FLAG-Rps3 was expressed in E. coli, affinity purified, and incubated for 30 min at 4 °C in the presence (+) or absence (−) of purified His6-Yar1. Thereafter, samples were subjected to centrifugation at 200,000 × g for 1 h, and equal amounts of pellet and supernatant fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. D, overexpression of Yar1 increases the solubility of Rps3 in yeast cells. (−), expression of plasmid encoded FLAG-Rps3 under the control of the CUP1-promoter was induced in a yar1Δ strain for 30 min. (+), in addition, plasmid encoded Yar1 was overexpressed from an ADH1-promoter. After mechanical disruption of the cells, lysates were centrifuged at 200,000 × g for 1 h, and equal amounts of pellet and supernatant fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting.