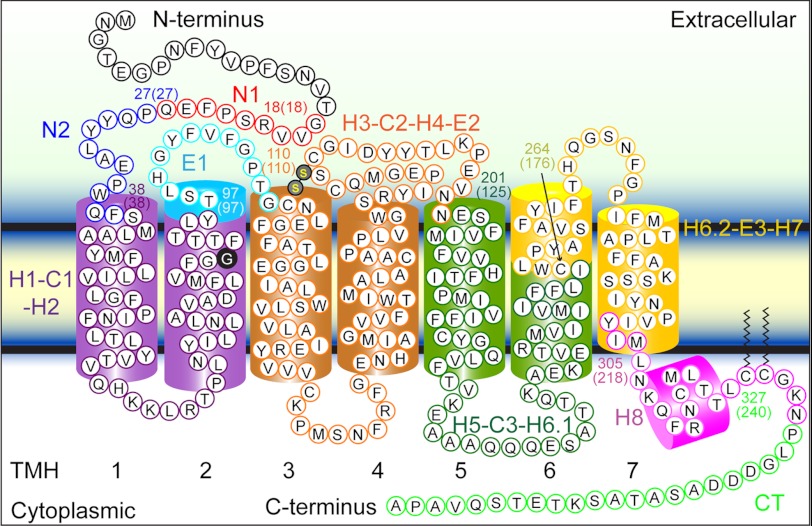
FIGURE 4.
Stable structural segments of wild-type and G90D mutant rhodopsin detected by SMFS. The most probable contour length of each major force peak was used to localize the corresponding structural segment in wild-type rhodopsin (Table 1). Within the accuracy of the measurements, the structural segments observed for wild-type and G90D mutant rhodopsin were identical (Table 1). Each structural segment is colored and named on the secondary structure. The boundary amino acid residues for each segment are numbered, and the contour length of the corresponding force peak is given in parentheses. Transmembrane α-helices (TMH) 1–7 are numbered.