Figure 5. Postnatal deletion of Pdk1 in pyramidal neurons does not induce deficits in synaptic plasticity.
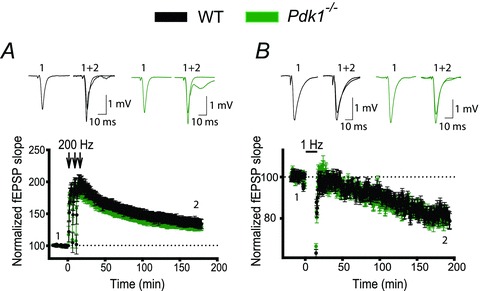
A and B, synaptic plasticity is not perturbed in Pdk1−/− mice. The mean fEPSP slope versus time before and after induction of LTP (A) or LTD (B) in slices from WT and Pdk1−/− mice did not differ. Insets show representative fEPSP traces before and 180 min after induction of synaptic plasticity.
