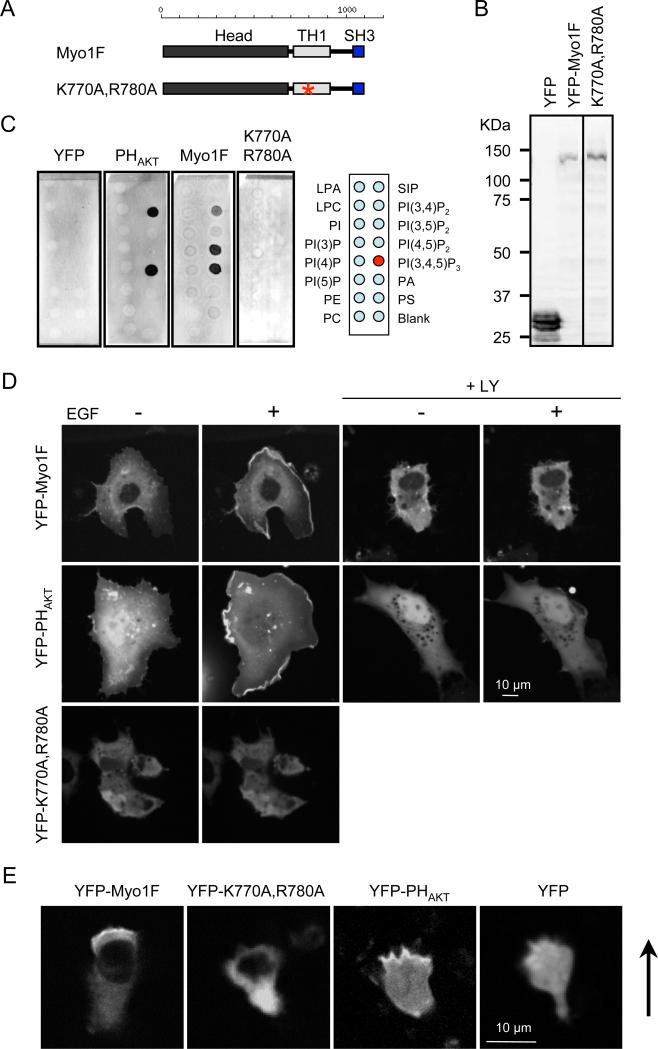
Figure 4. PIP3 regulates the intracellular localization of human myosin IF.
(A) The domain structure of human myosin IF. An asterisk indicates the location of the mutations introduced in the TH1 domain (K770A, R780A). (B) Immunoblotting of whole cell lysates prepared from COS-7 cells expressing YFP-human myosin IF using anti-GFP antibodies. (C) Lipid dot blot assays show that interactions between YFP-human myosin IF and PIP3 depend on the TH1 domain. YFP was used as a negative control and PHAKT-YFP was used as a positive control. Images are representative of >3 independent experiments. (D) Localization of YFP-human myosin IF, YFP-human myosin IF (K770A, R780A), and PHAKT-YFP was examined in COS-7 cells before and after EGF treatment (n = 3 experiments, more than 10 cells analyzed in each experiment). In the presence of LY294002, EGF-stimulated membrane recruitment of YFP-myosin IF and PHAKT-YFP was blocked (+LY). (E) Localization of YFP-human myosin IF, YFP-human myosin IF (K770A, R780A), PHAKT-YFP, and YFP was evaluated in HL-60 cells stimulated by fMLP (n = 3 experiments). Arrows indicate the direction of cell migration.