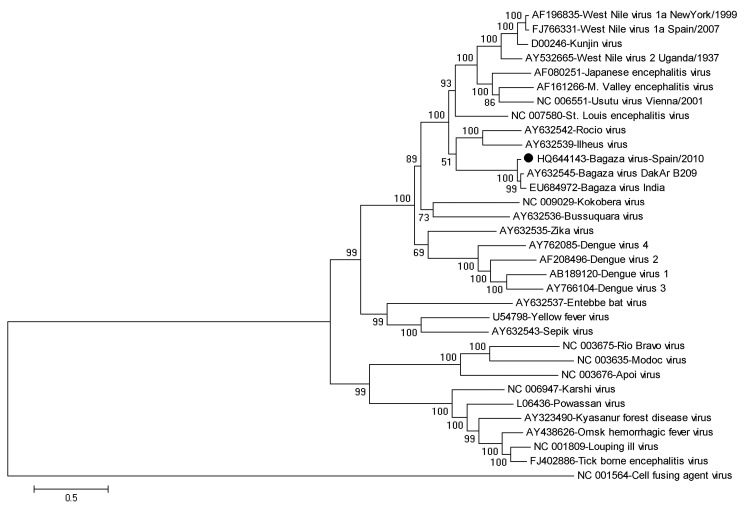
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic relationships between a full-length genomic sequence for Bagaza virus identified in Cádiz, Spain, 2010 (solid circle) and 32 full-length flavivirus sequences, including 2 Bagaza virus isolates from GenBank. The phylogenetic tree was inferred by using the maximum-likelihood method. Percentage of 500 successful bootstrap replicates is indicated at the nodes. Evolutionary distances were computed by using the optimal general time reversible + Γ + proportion invariant model. A discrete Γ distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites (5 categories, G parameter = 2.0552). The rate variation model enabled some sites to be evolutionarily invariable (+I, 10.1524% sites). The tree is drawn to scale, and branch lengths are indicated as number of nucleotide substitutions per site. There were 9,803 positions in the final dataset. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted by using MEGA5 (www.megasoftware.net). GenBank accession numbers are indicated beside each isolate/strain name.