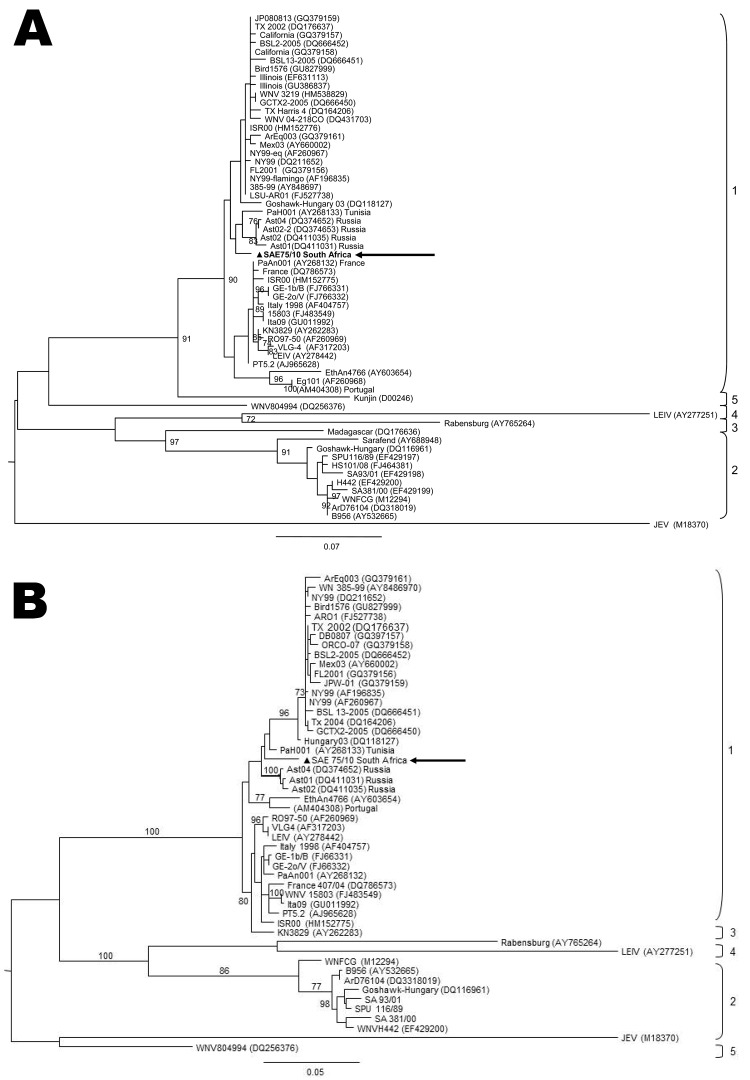
Figure 2.
Maximum-likelihood comparison of a partial section of the E-protein gene (A) and NS5 gene (B) of West Nile virus (WNV) lineage 2 strains isolated in South Africa (SA) in 2010 from a mare with fatal neurologic disease and representative sequences of other WNV lineages from various regions of the world. The lineage 1 strain, SAE75/10, identified in South Africa is indicated by a triangle and arrow. Sequences were aligned with MAFFT version 6 (http://align.bmr.kyushu-u.ac.jp/mafft/software) and edited with BioEdit version 7.0.9.0 (www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit). Maximum-likelihood midpoint rooted trees were drawn by using PHYML (www.atgc-montpellier.fr/phyml) under 100 bootstrap repetitions and the HKY codon position substitution model and drawn to scale with the bars indicating 0.07 nt substitutions. Only bootstrap values >70 are shown. Reference strains used from GenBank that were most closely related to SA L1: PAH001, Tunisia (AY268133); Ast04-2-824A, Russia (DQ374652); Ast02-2-25, Russia (DQ374653); Ast02-2-692, Russia (DQ411031); Ast01-187, Russia (DQ411035); Ge1b/B, Spain (FJ766331); GE-2o/V, Spain (FJ766332); WNV Italy-1998-equine, Italy (AF404757); WNV15803, Italy (FJ483549); and Ita09, Italy (GU011992).