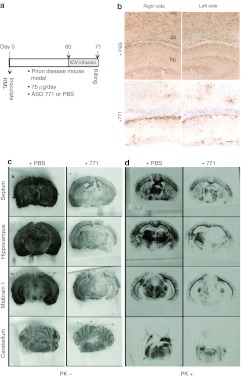
Figure 7.
Treatment with ASO 771 at the midpoint of disease reversed PrPSc deposition but caused atypical illness. (a) Experimental design. On day 0, FVB mice were inoculated with RML prions. Beginning at 60 dpi, ASO 771 was delivered via ICV at 75 µg/day for 11 days, when they developed atypical illness. Mice were killed at 71 dpi and their brains analyzed for (c) PrPC and (b,d) PrPSc. (b) Immunohistochemistry for PrPSc was performed on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections through the hippocampus by the hydrolytic autoclaving method and with recFab HuM-P. (c,d) Histoblots indicate that both PrPC and PrPSc were reduced following administration of ASO 771. Reduction of PrPC appeared more prominent on the cannulation side, whereas PrPSc depletion occurred bilaterally. Sections were left undigested to visualize total PrP levels as shown in c or subjected to GdnHCl denaturation and PK digestion to visualize PrPSc levels as shown in d, then stained with the D18 antibody. Bar in b represents 50 µm and applies to all the images in the panel. ASO, antisense oligonucleotide; cc, corpus collosum; hp, hippocampus; ICV, intracerebral ventricular; nc, neocortex; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PrPC, cellular prion protein; PrPSc, disease-causing prion protein.