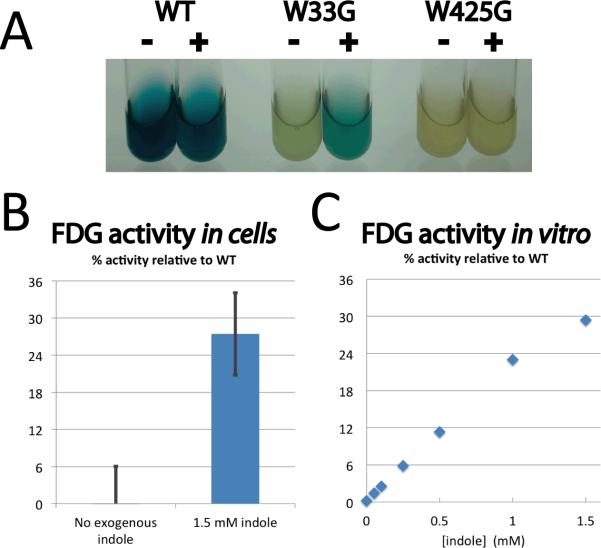
Figure 4. Indole rescue in living cells.
(A) E. coli cells expressing β-gly supplemented with X-gal substrate for qualitative detection of activity. Addition of indole (indicated with +/−) affects neither wild type β-gly activity (left pair, positive control) nor β-gly W425G activity (right pair, negative control). Only β-gly W33G (center) shows indole-dependent activity. All tubes contain 196 μM X-gal and 1 mM IPTG; those marked with a “+” additionally contain 2 mM indole. (B) Quantification of β-gly activity in E. coli cells supplemented with FDG substrate. Fraction of product formation by β-gly W33G after 30 min is reported relative to wild type β-gly. Four experimental replicates were averaged; error bars represent the standard error. (C) The analogous experiment was carried out in vitro to determine the maximal activity relative to the wild type enzyme that could be expected from addition of 1.5 mM indole to the cell cultures.