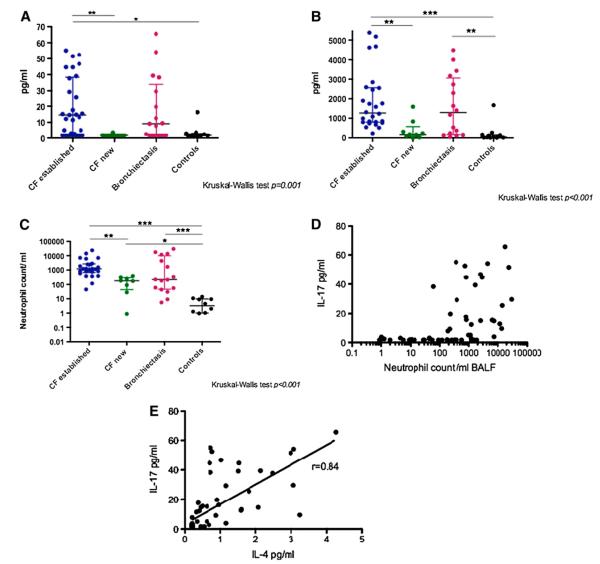
Figure 5.
(A) IL-17 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). IL-17 levels were significantly different (Kruskal-Wallis [KW] P = 0.001) across disease groups. Patients newly diagnosed with cystic fibrosis (CF) had levels (median [interquartile range] 1.7 [1.7–1.74] pg/ml) similar to control subjects (1.7 [1.7–3] pg/ml; P = 0.3). Patients with established CF had significantly higher levels (14.6 [2.2–38.4] pg/ml) than both of these groups (P < 0.01 vs. new CF, P < 0.05 vs. control subjects). Levels in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis (9.1 [1.7–34] pg/ml) appeared raised above control and newly diagnosed CF values, but after correction for multiple comparisons, this did not reach statistical significance. There was no difference in IL-17 levels between patients with established CF and patients with non-CF bronchiectasis. (B) IL-8 levels in BALF. IL-8 levels are significantly different across disease groups (KW P < 0.001). Levels in patients with established CF are significantly higher than control subjects and patients newly diagnosed with CF (P < 0.001, P < 0.01, respectively), levels in patients with non-CF bronchiectasis are also significantly higher than control subjects (P < 0.01). (C) Neutrophil counts in BALF. Neutrophil counts are significantly different across disease groups (KW P < 0.001). Neutrophil counts in patients newly diagnosed with CF are already significantly higher than control subjects (P < 0.05). (D) There is a significant correlation between BALF IL-17 levels and BALF neutrophil counts (P < 0.001, R = 0.6) (x-axis is a logarithmic scale). (E) Unexpected significant correlation of IL-17 with IL-4 in BALF (P < 0.001, R = 0.84).