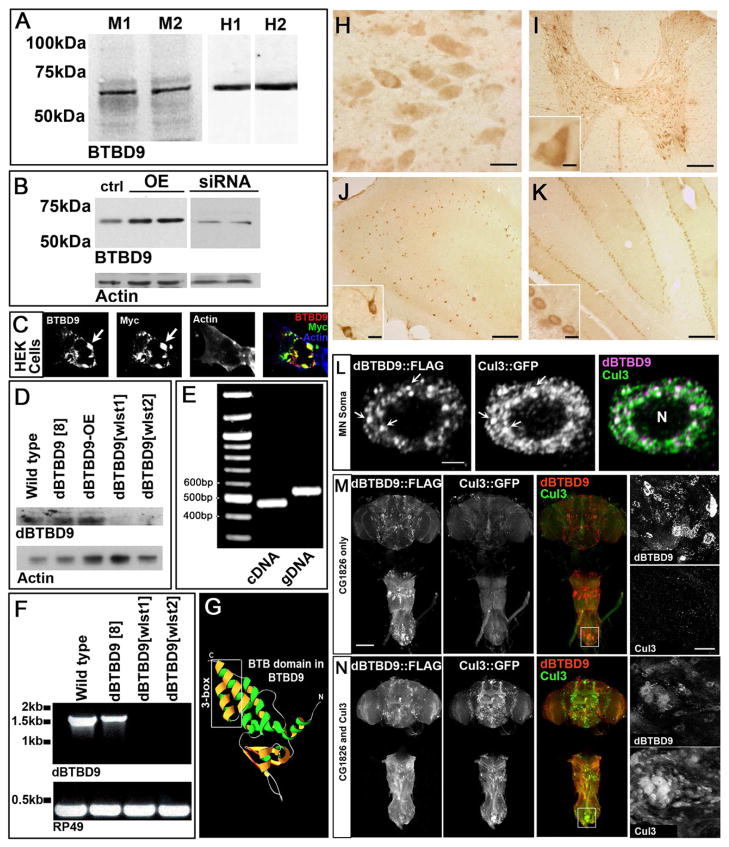
Figure 1. BTBD9 is a cytosolic Cullin-3 adaptor that is expressed widely in the mammalian and Drosophila nervous system.
(A) Western blots of two independent mouse and human brain protein extracts probed for BTBD9. (B) Protein extracts from HEK cells showing basal, over-expression and siRNA mediated knockdown of BTBD9. (C) HEK cell transfected with Myc-tagged BTBD9 and stained for BTBD9, Myc and Actin. Arrows indicate BTBD9 and Myc co-localization. (D) Western blots from Drosophila adult brain protein extracts probed for dBTBD9. dBTBD9[8] is a precise excision control, dBTBD9[OE] is pan-neuronal over-expression of dBTBD9 and dBTBD9[wlst1] and dBTBD9[wlst2] are null alleles. (E) PCR using cDNA and gDNA extracted from the adult Drosophila brain as template with intro-spanning primers for dBTBD9. (F) RT-PCR from mRNA isolated from control and excision alleles of dBTBD9. The ribosomal gene rp49 is used as a control. (G) Homology model of the N-terminal half of BTBD9 based on the crystal structure of SPOP showing the Cul-3 interacting 3-box. (H) BTBD9 staining in human nucleus basalis demonstrates cytoplasmic localization. Scale bar = 20μm. BTBD9 staining (I) throughout the grey matter of the rat spinal cord including motor neurons (inset shows enlarged view), (J) rat hippocampus (enlarged inset shows neurons of the CA1 region), and (K) Purkinje cells of the cerebellum (inset shows enlarged view). Scale bar = 200μm in (I–K) and 20μm (I–K insets). (L) A single neuron in the adult fly CNS stained for dBTBD9 (FLAG tagged dBTBD9) and Cul-3 (GFP tagged Cul-3) showing extensive co-localization (arrows). Scale bar = 2μm (M) CNS of an adult fly expressing FLAG tagged dBTBD9 (enlarged inset shows dBTBD9 aggregates). (N) CNS of a fly expressing both dBTBD9 and Cul-3, (inset shows enlarged view). Scale bar = 100μm. (See also Figure S1)