Figure 4. Relationship between brain response to milkshake vs. tasteless and other variables.
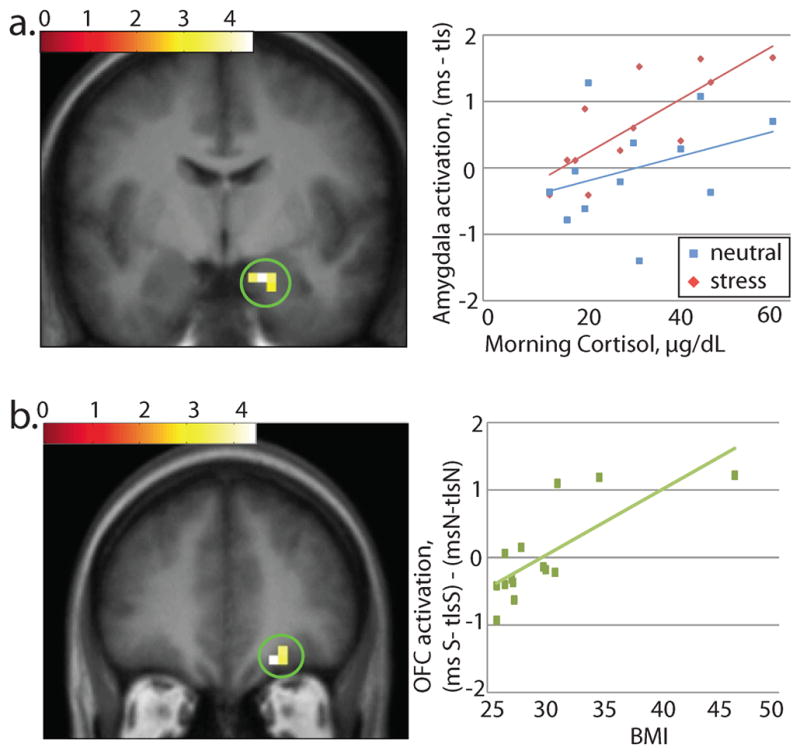
a. Basal cortisol measurements across subjects showed a relationship with brain response to milkshake vs. tasteless in the stress condition, but no relationship with response to the same contrast in the neutral-relaxing condition, in right amygdala (20, −4, −20). Post-hoc tests showed the strength of this correlation in the peak voxel to be r2 = 0.62 in stress and r2 = 0.12 in neutral-relaxing. Effect is significant at p=0.044 across the amygdala ROI.
b. In the right OFC (20, 40, −16), brain response to milkshake vs. tasteless in the stress vs. the neutral-relaxing condition was correlated with BMI with a strength of r2 = .059. Effect is significant at p=.043 across the midbrain & OFC ROI.
