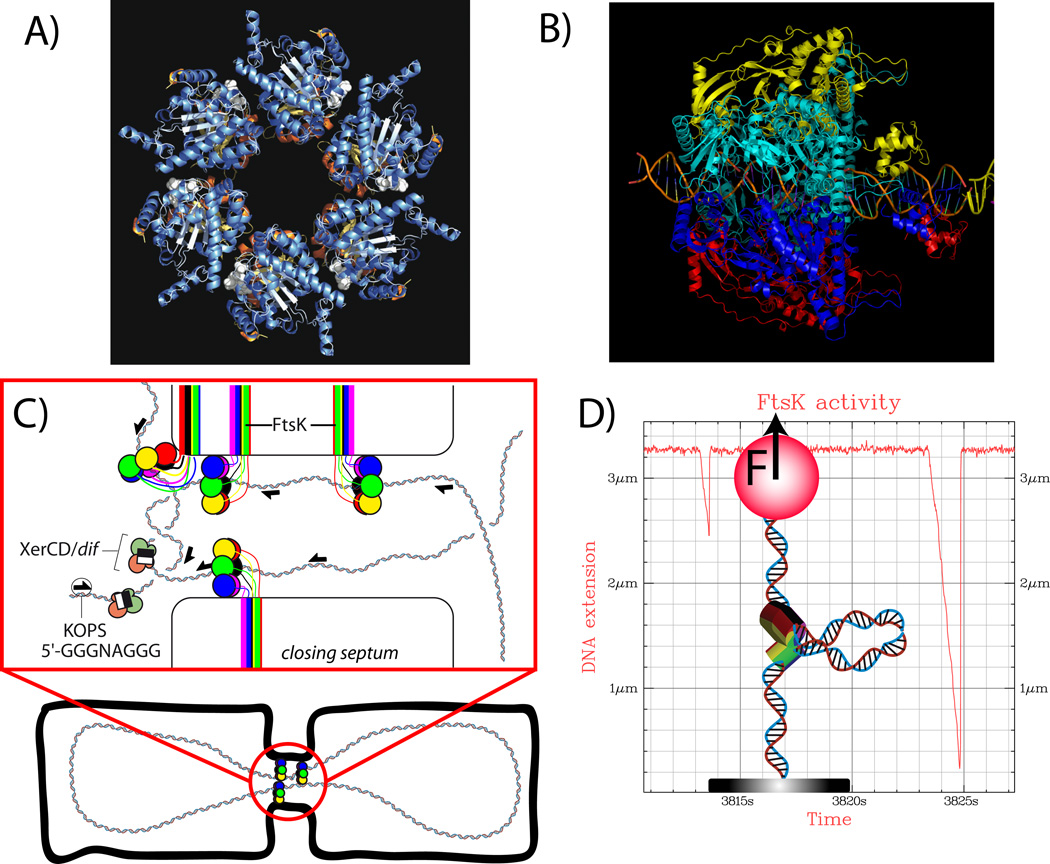
Figure 1.
A) Structure of FtsK : α and β domains of FtsK form an hexameric complex [11]. B) The hexamer has a central hole that allows the pumping of DNA during bacterial cell division. Central DNA and γ domain have been modeled onto the structure of A). Images from A) and B) were provided by D. Sherratt. C) FtsK localizes at the septum and catalyzes XerCD recombination at dif sites to resolve dimers produced by homologous recombination[5]. The exact structure of FtsK at the septum is not yet known but specific pores, formed by the membrane bound N terminal part of the proteins, are not required [10]. D) FtsK activity can be studied in vitro using optical or magnetic tweezers[15,16]. When FtsK is active it forms a loop that transiently shortens DNA extension. Distribution of changes in extension gives the processivity of the motor. Distribution of the slopes gives the speed. Both can be studied as function of ATP concentration, force, sequence, etc.