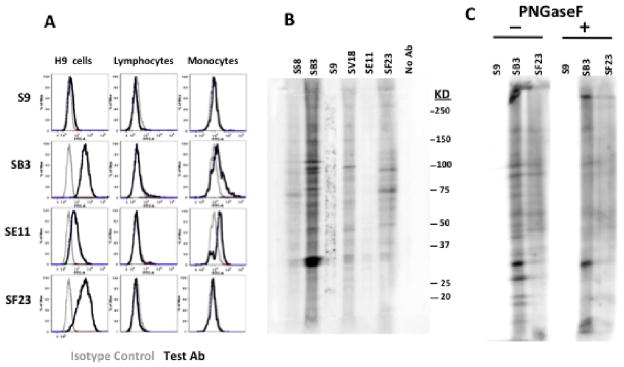
Figure 5. Binding of anti-GBS mAbs to lymphoid cells and monocytes.
(A) Flow cytometry was performed to measure binding to cell-surface antigens on H9 lymphoma cells, and freshly explanted peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell number is on the vertical axis, fluorescent intensity on the horizontal. Each graph compares binding of the test mAb (black) to an isotype-matched control mAb (grey). Lymphocytes and monocytes were examined together, and the cell populations segregated on the basis of forward and side scatter characteristics. (B and C). Immunoblots were performed on H9 cell lysates. In B the lysates were not treated with any enzymes, in C cells were digested (or not) with PNGaseF to remove carbohydrate determinants from glycoproteins. Lysates were blotted onto membranes and incubated with the indicated antibodies, followed by detection with alkaline-phosphatase conjugated anti-mouse Ig and chemiluminescent detection.