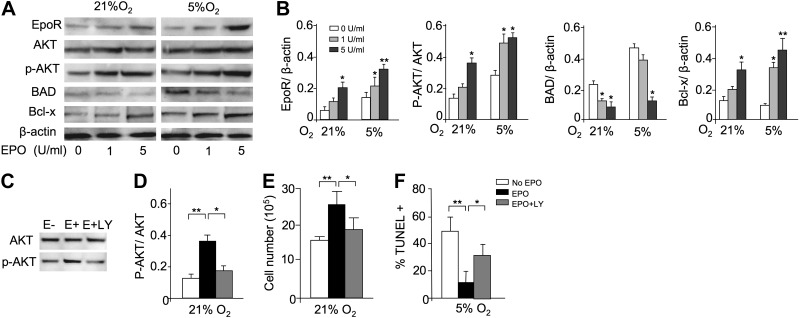
Figure 7.
EPO protection and AKT-signaling pathway in myoblasts. A) To confirm the profile expression array results, Western blot analysis for EpoR, AKT, phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT), BAD, and Bcl-x was performed for C2C12 cells cultured with EPO (0, 1, 5 U/ml) for 24 h at 21 and 5% O2; β-actin protein expression was used as internal control. B) Western blot analysis results were quantified for cells cultured without EPO (open bars) and with EPO at 1 U/ml (shaded bars) and at 5 U/ml (solid bars) and normalized to β-actin. C–F) C2C12 cells were cultured for 24 h without EPO (open bars) and with EPO (5 U/ml; black bars) and with EPO plus LY-294002 (50 μM; shaded bars), an inhibitor of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. LY-294002 inhibited the EPO-induced AKT phosphorylation, determined by Western blot analysis for AKT and p-AKT (C, D), and reversed the proliferative effect of EPO at 21% O2 (seeded initially at 1×106 cells/well in 6-well plates; E) and the antiapoptotic EPO effect at 5% O2, as indicated by percentage TUNEL+ (F). Quantification of Western blot analysis results are shown as p-AKT/AKT (D). **P < 0.01.