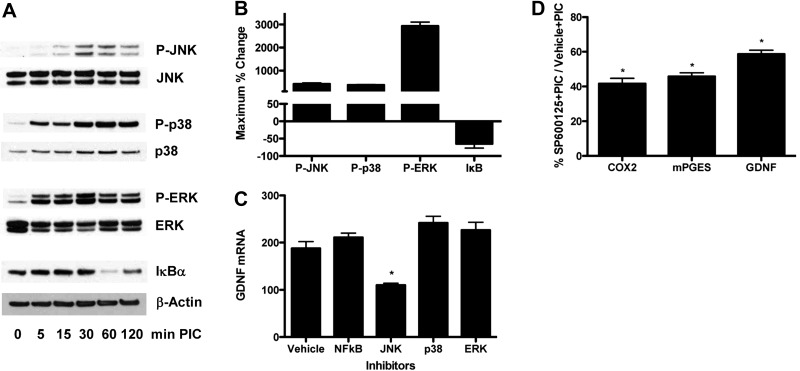
Figure 4.
JNK signaling selectively but partially mediates PIC-induced GDNF expression and PG pathway activation. A) WT murine primary astrocytes were incubated with 20 μg/ml PIC for up to 120 min, sampled at the times shown, and analyzed by Western blot for activation of JNK, p38, and ERK by assaying phosphorylation and IκBα by assaying its degradation. Respective blots were stripped and then reprobed with JNK, p38, ERK, or β-actin antibody. B) Average ± se maximum percentage change from experiments in panel A was calculated by densitometric scanning of blots. C, D) WT murine primary astrocytes were pretreated with vehicle or inhibitor of JNK (SP600125, 10 μM), p38 (SB202190, 10 μM), ERK (U0126, 10 μM), or NF-κB (BAY11-7085, 2 μM) for 30 min, followed by addition of 20 μg/ml PIC for an additional 18 h. RNA was isolated, and quantitative real-time PCR was performed, and results were normalized to 18s rRNA. C) Expression of GDNF presented as average ± se (n=6). ANOVA had P < 0.0001. Bonferroni-corrected paired comparison was significant for JNK inhibitor vs. all other inhibitors or vehicle. Vehicle vs. all other inhibitors had P > 0.05. *P < 0.001; Bonferroni posttest. D) Expression of COX-2, mPGES, and GDNF presented as average percentage of cultures exposed to vehicle (100%) rather than JNK inhibitor (SP600125) before TLR3 activation with PIC. Unpaired t tests were performed on raw data rather than percentages. *P < 0.001.