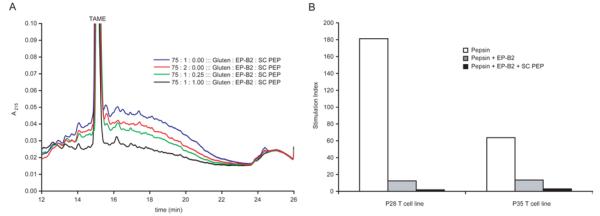
Figure 5.
Detoxification of gluten from whole-wheat bread using an acid-active two-enzyme glutenase. Whole-wheat bread was digested with pepsin supplemented with varied concentrations of EP-B2 ± SC PEP for 60 min at pH 4.5 at 37 °C. A. Reversed-phase HPLC analysis of effect of EP-B2 ± SC PEP on gluten digestion. The broad peak between 12.5-22 minutes reflects immunogenic gluten peptides 9-22 residues in length. Note that ordinate axis is scaled to highlight the incremental effect of increasing SC PEP; this view truncates the TAME internal standard peak. B. T cell proliferation assays measuring antigen content of whole-wheat bread digests. Pepsin (0.6 mg/mL) was supplemented with EP-B2 (200 U) ± SC PEP (0.5 U). Gastric digests were treated for an additional 10 min under duodenal conditions (0.375 mg/mL trypsin and chymotrypsin and 0.075 mg/mL elastase and carboxypeptidase A at pH 6.0 at 37 °C) to solubilize all remaining T cell epitopes. P28 and P35 are T cell lines expanded from celiac patient intestinal biopsies. A stimulation index of 1 indicates background levels of proliferation.