Table 2.
In Situ Intramolecular Schmidt Reaction of New Substrates[a]
| Entry | Halide | Product | Yield (%) |
Recovery (%) (Azide/Halide) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
||||
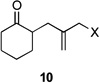
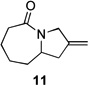
| 1 | 10a | X = Cl | 11 | 51 | –/14 |
| 2 | 10b | X = Br | 11 | 53 | – |
 |
 |
||||
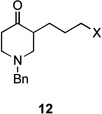
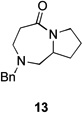
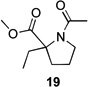
| 3 | 12a | X = Cl | 13 | 77[b] | –/11 |
| 4 | 12b | X = Br | 13 | 61[b] | – |
| 5 | 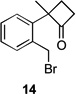 |
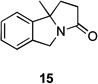 |
54 | – | |
| 6 | 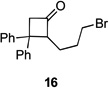 |
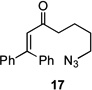 |
83 | – | |
| 7 | 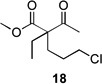 |
 |
trace | 66/– | |
| 8 | 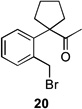 |
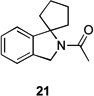 |
67 | – | |
| 9 | 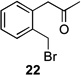 |
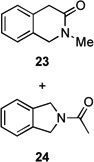 |
40 (23:24 = 3:1) |
33/– | |
Conditions: 1. Substrate 2M in CH3CN, 1.1 equiv. NBu4N3, 300 W MWI, 50 µL/min. 2. TFA (3 mL, excess) 50 µL/min, 40 PSI back pressure.
Reaction was performed at 125 W.
