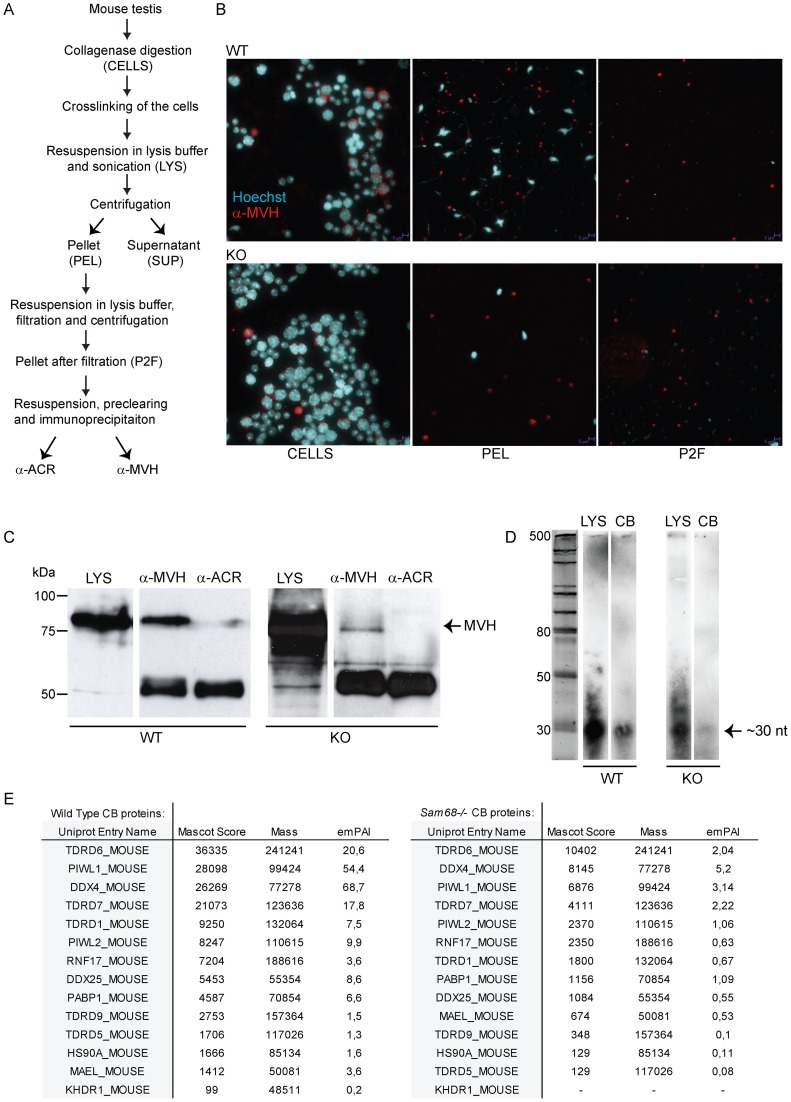
Figure 6. Isolation and analysis of chromatoid bodies from male germ cells.
(A) Schematic representation of the CB isolation protocol. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of different steps of CB immunoprecipitation experiment, comparing Sam68 wild type (WT) and knockout (KO) extracts. Cells were stained with an anti-MVH antibody (red) and with Hoechst to detect nuclei. CELLS = cells before lysis; LYS = lysate; PEL = pellet fraction; P2F = pellet fraction after filtration. (C) Immunoblotting of the CB extracts with anti-MVH antibody to validate the success of the purification. The less intensive signal in the knockout CB fraction indicates the lower number of CBs isolated from the knockout testes compared to the control. anti-ACR, negative control IP; anti-MVH, CB IP. (D) RNA gel to demonstrate the presence of piRNAs. Total RNA was extracted from the the lysate (LYS) and CB IPs (CB), radiolabelled and run into a polyacrylamide gel in. (E) Mascot analysis of the main CB components. All major CB proteins were present in the knockout CBs. The uniprot entry name KDHR_MOUSE equals to SAM68.