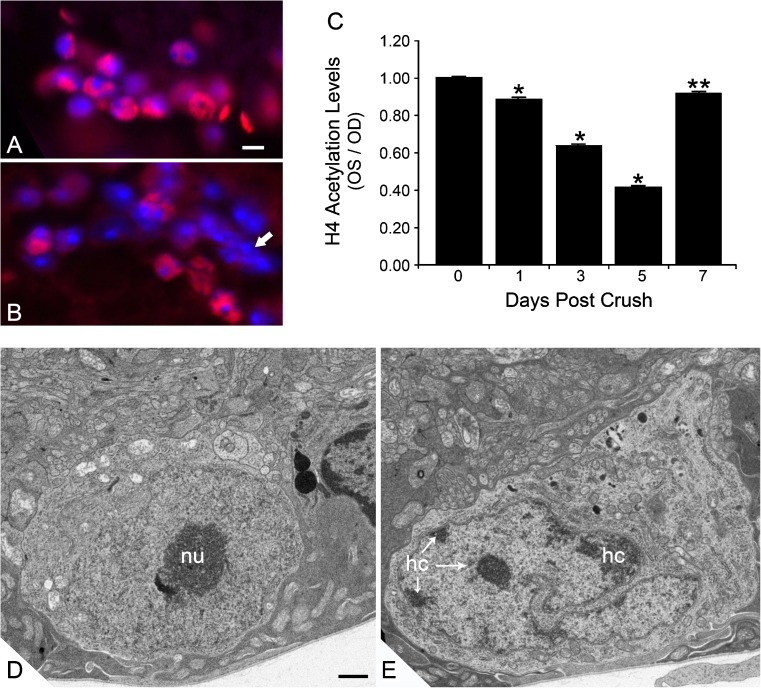
Fig. 2.
Histone deacetylation and nuclear changes in RGCs after ONC. Immunofluorescent labeling of acetylated histone H4 (AcH4) in the ganglion cell layer of a control mouse eye (a) and an eye 5 days after optic nerve crush (b). Nuclei have been counterstained with DAPI. Eyes with crush exhibit nuclei with reduced or absent staining for AcH4. Nuclear morphology often demonstrates highly condensed chromatin (arrow in b). Scale bar = 10 μm. c Quantification of histone H4 acetylation in the ganglion cell layer of mouse eyes after ONC. Data from this experiment were collected by measuring the pixel density of AcH4 label per total area of each nucleus examined and normalizing this value to the pixel density of unaffected nuclei in the inner nuclear layer. The data are depicted as the ratio of experimental (OS) and control (OD) retinas after ONC. *P ≤ 0.0001 and **P = 0.041 (OS vs. OD at given time point). Transmission electron micrographs of control (d) and experimental (e) mouse retinas. Images were taken in the ganglion cell layer of eyes 5 days after ONC. Control eyes d exhibit round or oval nuclei with lightly staining euchromatin and prominent nucleoli (nu). In crush eyes, nuclei predominantly appear highly convoluted and exhibit the formation of varying degrees of heterochromatin (hc), typically forming along the inner side of the nuclear envelope. Scale bar = 500 nm. c was reprinted from [21], which is an open access journal