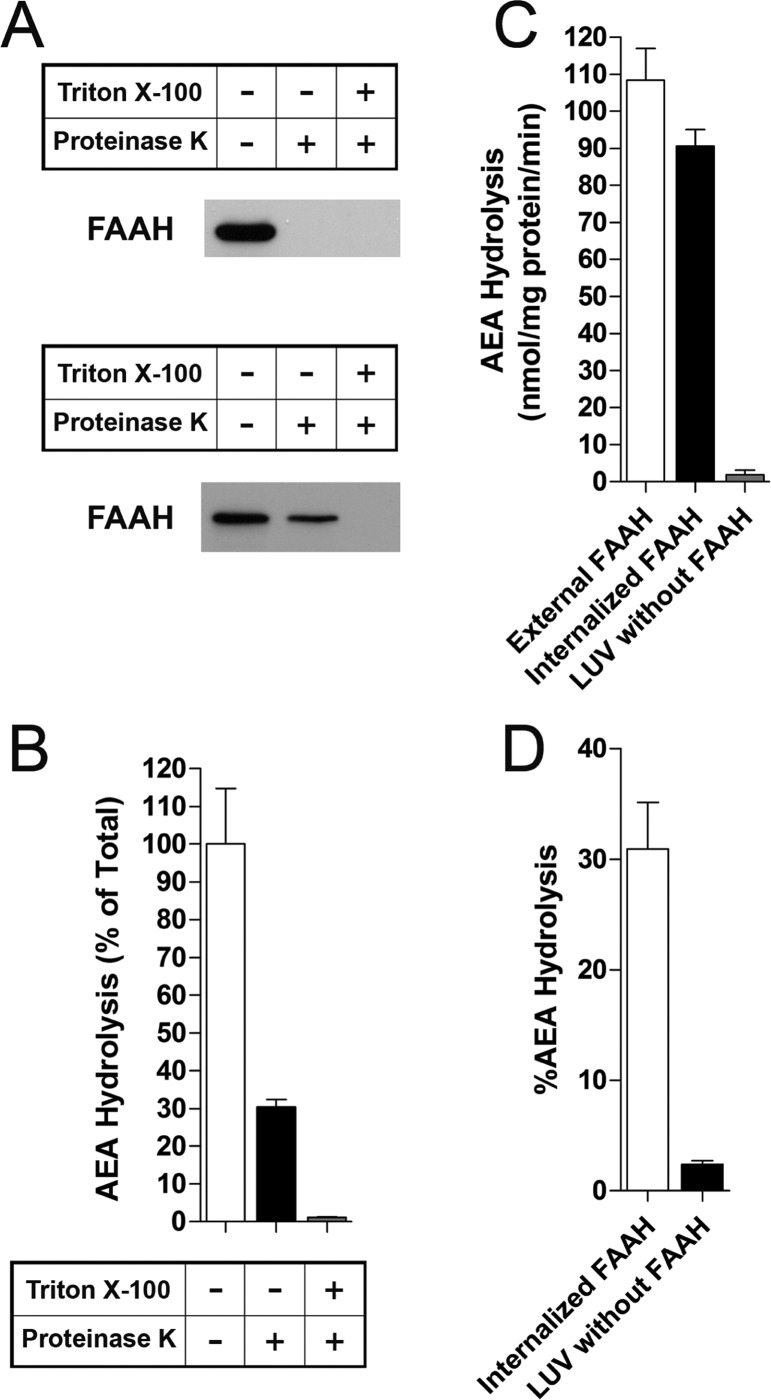
Figure 2.
Characterization of LUVs with internalized FAAH. (A) Treatment of LUVs with 30 μg/mL proteinase K completely cleaves externally facing FAAH (top panel). When added to the lipid mixtures before vesicle formation to permit internalization, only noninternalized FAAH is susceptible to proteinase K cleavage (bottom panel). Addition of 0.5% Triton X-100 to permeabilize membranes results in cleavage of trapped FAAH. (B) Hydrolysis of [14C]AEA by internalized FAAH is revealed following addition of proteinase K to cleave externally facing FAAH (n = 3). (C) Similar rates of [14C]AEA hydrolysis by externally or internally bound FAAH (n = 4). (D) Percentage of [14C]AEA hydrolysis of total AEA added to the reaction tubes by internalized FAAH (n = 5).