Fig. 4.
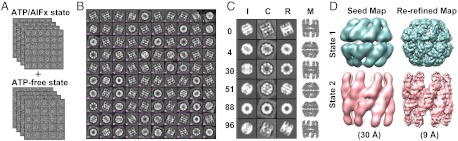
Separating heterogeneous conformations of lidless Mm-cpn with mixed states of EM particle images using the closed-state initial model. (A) Mixing 5000 ATP/aluminum fluoride-induced (closed) and 5000 ATP-free (open) states of lidless Mm-cpn raw particle images to generate the artificial heterogeneous EM dataset of 10,000 particles. (B) The 100 2D class averages that were generated from the 10,000 particle images. (C) Refinement results against six representative class averages exhibiting various conformational and orientational states such as open side view (Average #0), closed tilted view (Average #4), open top view (Average #30), closed side view (Average #51), closed top view (Average #88), and open tiled view (Average #96). Column I shows the projections of the initial closed-state model along the initially estimated orientations. Column C shows the target 2D experimental class averages. Column R shows the projection of each refined models (Column M) along the refined orientations. Column M shows the refined models after three iterations of NM-MC refinement (Materials and Methods). Note that for Average #30, the initially estimated orientation was not correct due to the large conformational difference between the initial model and the class average. After three iterations, both the correct orientation and conformation were obtained. (D) Seed maps generated from two clustered states of the refined models at 30 Å resolution (Left) and the re-refined maps at 9 Å resolution in which α-helices are visible (SI Materials and Methods, Figs. S8 and S9).