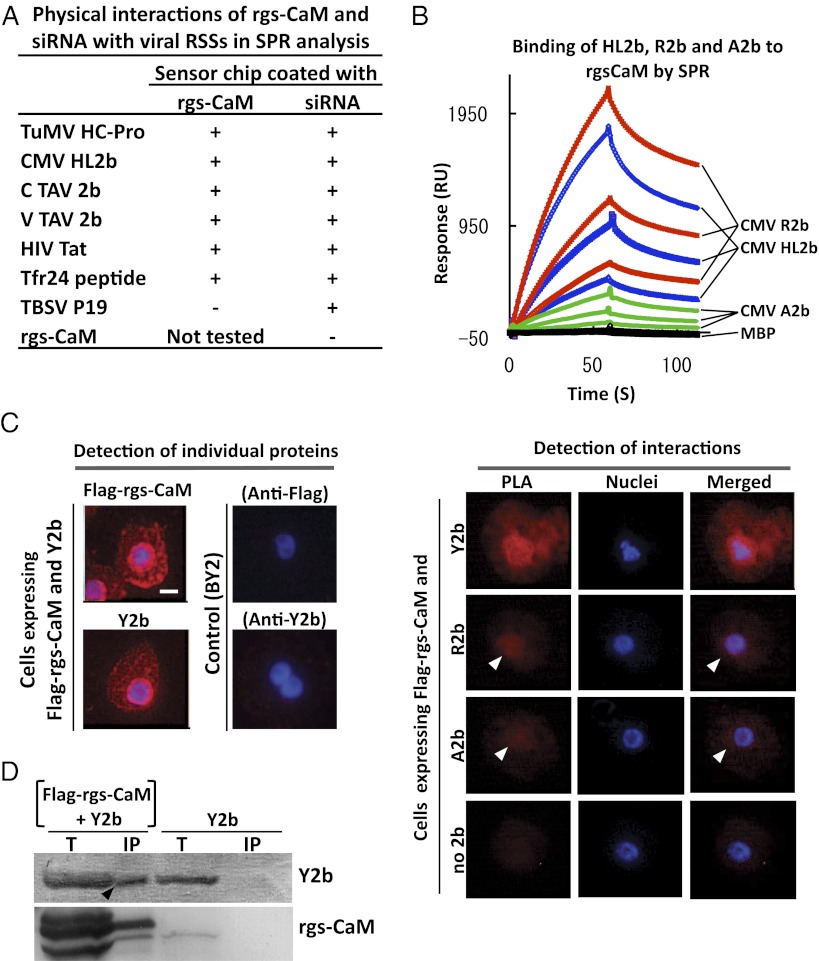
Fig. 1.
Interaction of rgs-CaM with viral RSSs. (A) Purified RSS proteins were tested for binding to immobilized rgs-CaM protein and siRNA by SPR analysis. Plus sign, interaction detected; minus sign, no interaction detected. (Raw data are in Fig. S1A.) (B) CMV-R2b, -A2b, or -HL2b (at 150, 75, and 37.5 μg/mL) fused with maltose-binding protein (MBP) or MBP alone was tested for binding to immobilized rgs-CaM by SPR. (C) Interactions between transiently expressed Flag–rgs-CaM and Y2b, R2b, or A2b were detected in the proximity ligation assay (PLA) as fluorescent signals in BY2 cells. Each of these proteins was individually detected by single recognition PLA with anti-Flag (Flag–rgs-CaM) and anti-2b (Y2b) antibodies (Left). In cells expressing Flag-rgs-CaM and Y2b, a PLA signal means interactions between the two (Right, PLA). Weaker PLA signals (white arrowheads) were also detected for rgs-CaM combined with other 2bs (R2b and A2b). Hoechst 33342-stained nuclei (Nuclei) and merged images (Merged) are also shown. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (D) Flag-tagged rgs-CaM (Flag–rgs-CaM) and its associated proteins were precipitated by anti-Flag antibody in crude extracts from tobacco infected with CMV/Y2b and either the PVX vector expressing Flag–rgs-CaM or the empty vector at 16 d postinoculation (dpi). Total (T) and precipitated proteins (IP) were fractionated by SDS/PAGE, and rgs-CaM and 2b were detected using specific antibodies. The 2b band in the IP fraction with PVX/Flag–rgs-CaM (arrowhead) indicates rgs-CaM interaction with 2b.