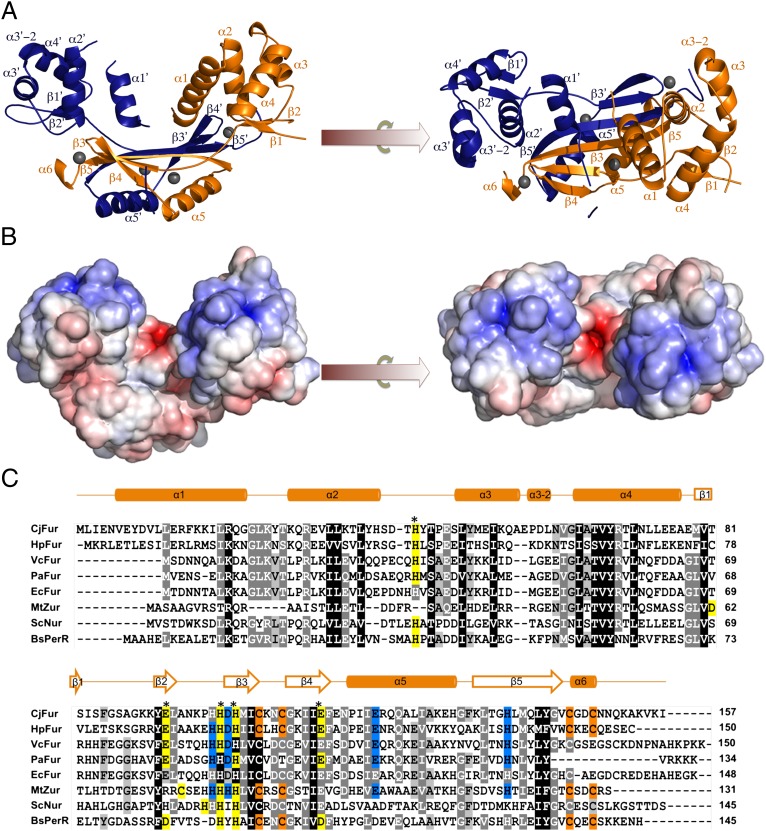
Fig. 3.
(A) Crystal structure of CjFur. Orthogonal views of the CjFur crystal structure in which protomers A and B are rendered in orange and blue, respectively. β-Sheets and α-helices are labeled accordingly, and zinc atoms are depicted as gray spheres. (B) Electrostatic surface potential of the CjFur crystal structure. Electrostatic potentials are contoured from +10 kbTe−1 (blue) to −10 kbTe−1 (red) (kb = Bolzmann's constant, T = temperature in Kelvin and e = charge of an electron). (C) Sequence alignment of Fur and Fur-like proteins. Sequence alignment of Fur proteins [C. jejuni (Cj), H. pylori (Hp), V. cholerae (Vc), P. aeruginosa (Pa), E. coli (Ec)] and of the Fur-like Zur from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MtZur), Nur from Streptomyces coelicolor (ScNur), and PerR from B. subtilis (BsPerR). Sequences were aligned using the ClustalW option in MEGA5 (35). CjFur secondary-structure elements are shown above the alignment. Asterisks indicate the residues involved in the predicted CjFur S2 site. S1 residues are shaded in orange, predicted S2 residues are in yellow, and S3 residues are in blue. Positions with 100% amino acid conservation are indicated by dark gray, 100–80% by medium gray, and 80–60% by light gray. kb, Bolzmann's constant; T, temperature in Kelvin; e, charge of an electron.