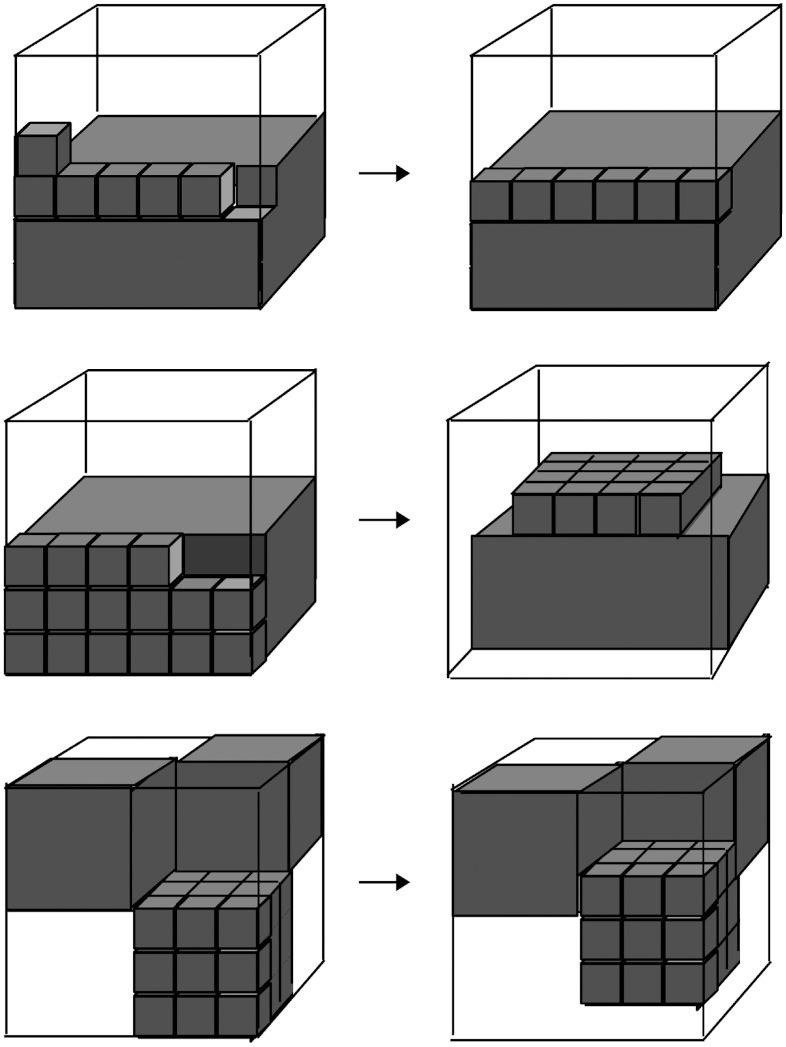
Fig. 4.
Minimal subvolume required for H/P swapping leading to lower energy. The schematic illustrates the three types of swapping for a cubic lattice of length 6. The hydrophobic residues (H) are shown in gray and the hydrophilic residues (P) are transparent for clarity purposes. The individual gray cubes denote the hydrophobic portion of the minimal subvolume n. The three types are (Top) swapping on one face, (Center) swapping involving multiple faces, and (Bottom) merging distinct hydrophobic regions. Note that the schematic illustrates the extreme cases in each of the three swapping categories; most configurations require smaller distortions.