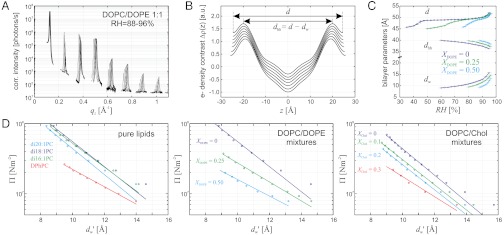
Fig. 2.
Bilayer structure and interactions as determined from electron density profiles: (A) Typical X-ray reflectivity data indicating eight clearly resolved orders of diffraction, (B) corresponding electron density profiles Δρ(z) (shifted vertically for clarity) reconstructed by aid of the swelling method, (C) structural data d,dhh,dw for DOPC/DOPE mixtures and (D) pressure-distance curves of all investigated lipids. The hydration properties of the branched-chain lipid DPhPC clearly deviate from those of di-monounsaturated PC lipids. Addition of DOPE or cholesterol facilitates dehydration and therefore close bilayer contact. For all investigated samples, stalk phase formation becomes favorable at dw < 9.0 ± 0.5 Å. In case of DOPC, curves Π(dw) from two independent measurements are shown.