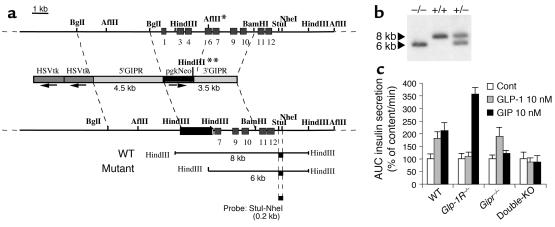
Figure 1.
Generation of Gipr–/– mice. (a) Diagram showing the mouse GIP-receptor gene, the GIP-receptor targeting vector, and the recombined allele. The genomic fragments diagnostic of homologous recombination using the external StuI-NheI probe are shown at the bottom of the figure. Positions of exons are marked as light gray boxes. In the mutant allele the AflII site denoted with * is replaced by a HindIII site on the 3′ end of the pgkNeo gene (marked with **). In the targeting vector, the arrows indicate the transcriptional orientation of the selection genes. (b) Southern blot analysis of the recombined alleles in mouse genomic DNA using the StuI-NheI probe. (c) Confirmation of receptor gene inactivation. Perifused isolated pancreatic islets from WT, Glp-1R–/–, Gipr–/–, or double-KO mice were challenged with successive 10-minute stimulation periods to 11.1 mM glucose, 2.8 mM glucose, 11.1 mM glucose + GLP-1 (10 nM), 2.8 mM glucose, 11.1 mM glucose + GIP (10 nM), and 2.8 mM glucose. Total insulin responses, quantified as AUC, are normalized for each genotype to the insulin response at 11.1 mM glucose alone, set at 100%. n = 4. Cont, control.