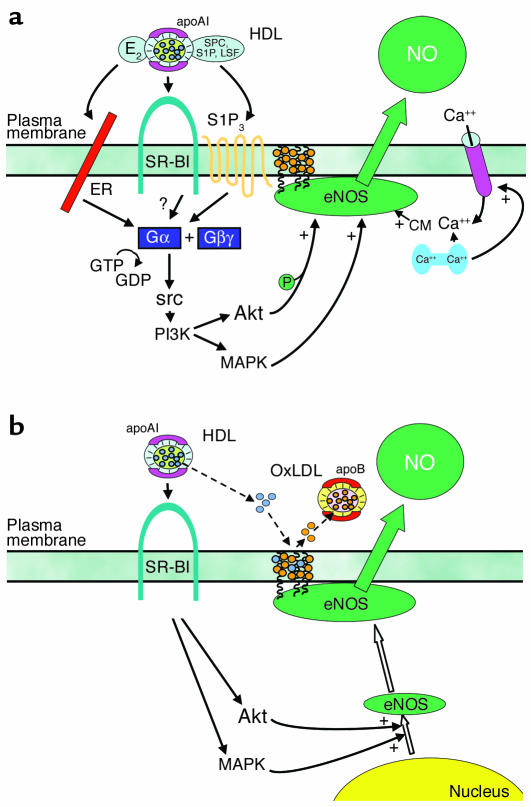
Figure 1.
HDL enhances NO production by eNOS in vascular endothelium. (a) HDL causes membrane-initiated signaling, which stimulates eNOS activity. The eNOS protein is localized in cholesterol-enriched (orange circles) plasma membrane caveolae as a result of the myristoylation and palmitoylation of the protein. Binding of HDL to SR-BI via apoAI causes rapid activation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase src, leading to PI3K activation and downstream activation of Akt kinase and MAPK. Akt enhances eNOS activity by phosphorylation, and independent MAPK-mediated processes are additionally required. HDL also causes an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration (intracellular Ca2+ store shown in blue; Ca2+ channel shown in pink), which enhances binding of calmodulin (CM) to eNOS. HDL-induced signaling is mediated at least partially by the HDL-associated lysophospholipids SPC, S1P, and LSF acting through the G protein–coupled lysophospholipid receptor S1P3. HDL-associated estradiol (E2) may also activate signaling by binding to plasma membrane–associated estrogen receptors (ERs), which are also G protein coupled. It remains to be determined if signaling events are also directly mediated by SR-BI (12, 15, 19, 22, 23). (b) HDL regulates eNOS abundance and subcellular distribution. In addition to modulating the acute response, the activation of the PI3K–Akt kinase pathway and MAPK by HDL upregulates eNOS expression (open arrows). HDL also regulates the lipid environment in caveolae (dashed arrows). Oxidized LDL (OxLDL) can serve as a cholesterol acceptor (orange circles), thereby disrupting caveolae and eNOS function. However, in the presence of OxLDL, HDL maintains the total cholesterol content of caveolae by the provision of cholesterol ester (blue circles), resulting in preservation of the eNOS signaling module (29–31).