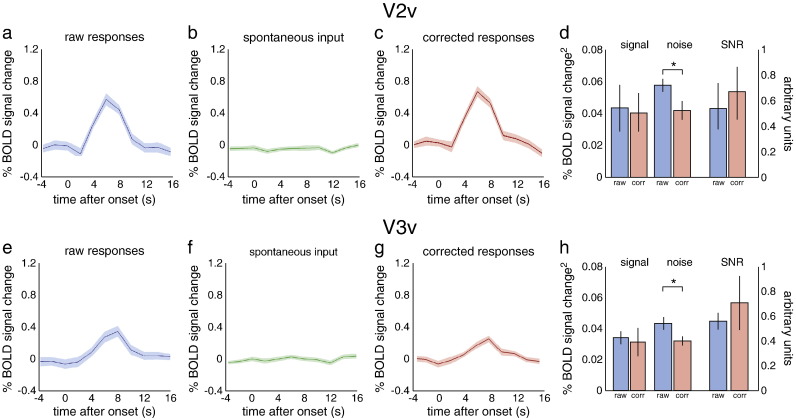
Supplementary Fig. 4.
Effect of spontaneous activity on BOLD response variability in V2 and V3. (a,e) The raw BOLD response is plotted for all trials of the same representative participant as in Fig. 3. (b,f) The spontaneous input measured in separately computed VOIproxy's for V2v and V3v. (c,g) Subtracting the spontaneous input reduced the variability in the evoked BOLD responses. (d,h) Signal power (left), noise power (middle), and SNR (right) in V2v and V3v for all participants before (‘raw’; in blue) and after (‘corr’; in red) subtracting the estimated spontaneous activity. The y-axis on the left in both graphs corresponds to the signal and noise power, the y-axis on the right to the SNR. Noise power was significantly reduced in both cases, yet SNR not significantly increased, after spontaneous activity subtraction. For details, see Fig. 3.