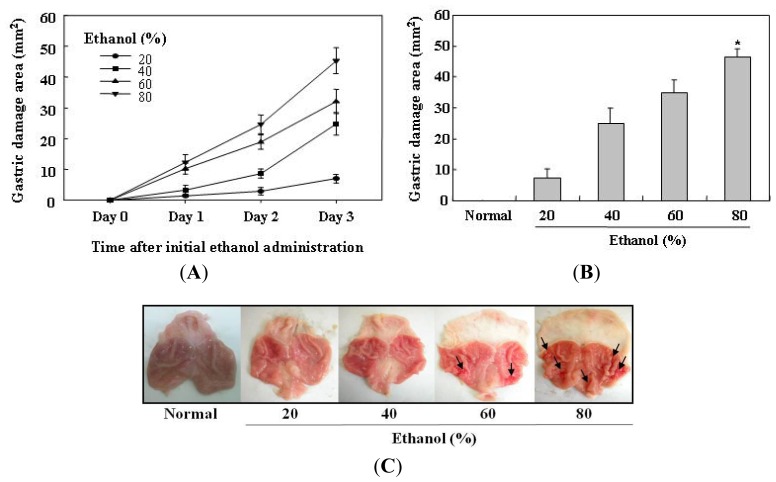
Figure 1.
Determination of optimal ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury model in rats. (A) Ulcerogenic effects in rats with various doses of ethanol, when administered over a 3 day period; (B and C) Various concentrations (20, 40, 60, and 80%) of ethanol were given by orogastric gavage for 3 days. Gastric damage area (mm2) was judged macroscopically by clear depth of penetration into the gastric mucosal surface. 80% ethanol induced the highest increase in the area of gastric damage. The arrows show the gastric mucosal lesions, such as erosions, bleeding, and ulcers. Values are expressed as the mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05, significantly different from the untreated normal rats.