Figure 2. Structural Analysis of the SUN-KASH Interaction.
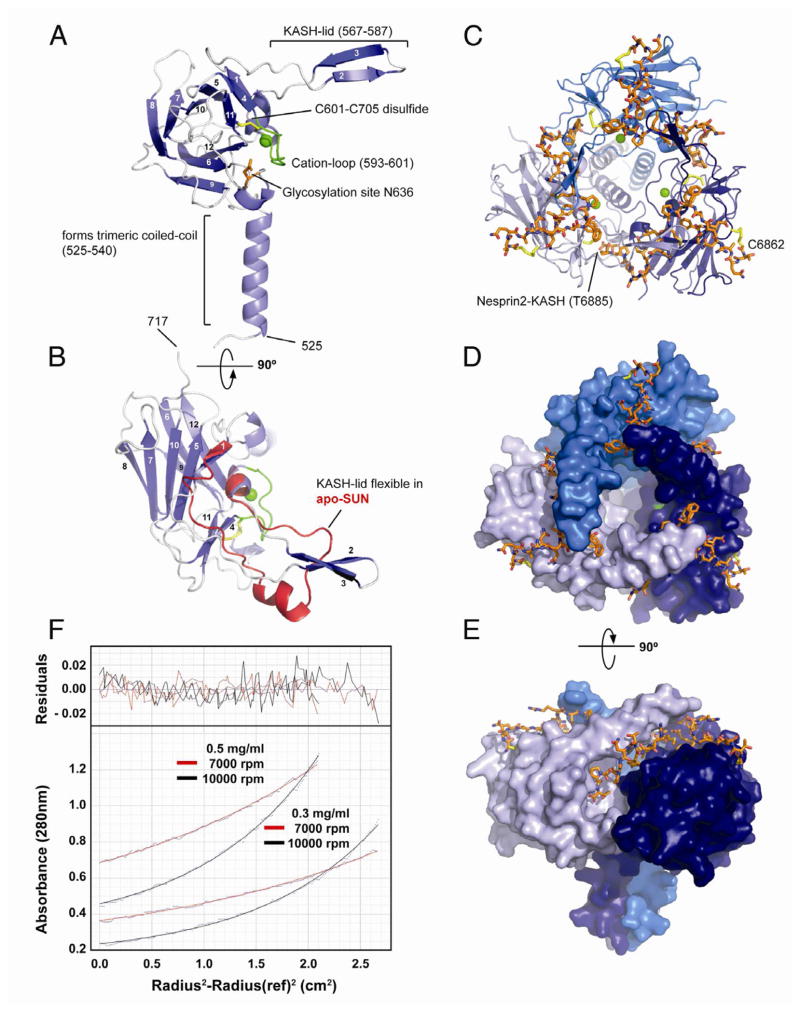
(A) Overview of a SUN2522–717 protomer isolated from its binding partners in the trimeric SUN-KASH complex. The protein is organized around a compact β-sandwich core, decorated with features important for function (labeled). Bound cation in green.
(B) Top view of the SUN2522–717 protomer (facing the outer nuclear membrane), rotated by 90° around the horizontal axis relative to the view in (A). The apo-protomer of SUN2522–717 is superimposed in red. Only the region with significant change is shown, coinciding largely with the KASH-lid.
(C) Top view of the trimeric SUN2522–717-KASH2 complex. The trimerizing SUN2 domains in cartoon representation and colored in shades of blue, the KASH2 peptide in orange. The peptide is covalently bound via a disulfide bridge between KASH2-C6862 and SUN2-C563.
(D) Same view as (C), but SUN2522–717 in surface representation, illustrating how each bound KASH2 peptide is clamped between two SUN2 protomers.
(E) Side view of the SUN2-KASH2 complex, illustrating the deep binding pocket on SUN2 into which the terminal four residues of the KASH peptide bind.
(F) Sedimentation equilibrium ultracentrifugation analysis of apo-SUN2335–717. The experiment was performed at two protein concentrations and two centrifugation speeds. Data was fitted for a single species. Fitted curves overlaid over primary data (dots) in red and black for the two speeds. Residuals in the upper panel. The mass was determined to be 131.3 ± 6.1 kDa, the calculated mass is 138 kDa for the trimer.
See also Figures S2, S4, S5.