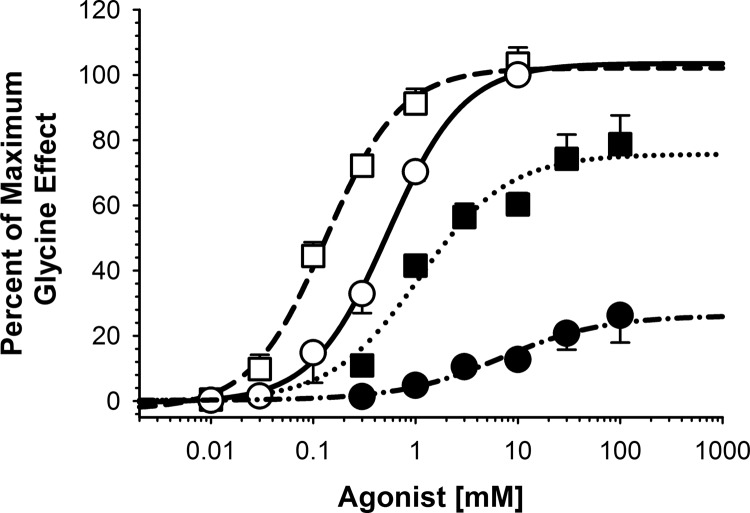
Fig. 1.
Isoflurane decreases agonist EC50 and increases taurine-mediated peak currents. Isoflurane shifts α1-homomeric GlyR glycine and taurine concentration-response curves to the left and increases the maximal response to the partial agonist. Open symbols represent glycine-mediated responses, and filled symbols show taurine-mediated responses. Circles represent agonist applied alone, with squares showing agonist + 1.1 mM isoflurane. Each line is a logistic fit to the respective set of data. Glycine activation of the GlyR produced an EC50 of 0.54 mM with a Hill coefficient (nH) of 1.2. The addition of 1.1 mM isoflurane decreased the EC50 to 0.13 mM and an nH of 1.2. Taurine alone had an EC50 of 6.9 mM, with an nH of 0.9, decreasing to an EC50 of 1.1 mM and an nH of 1.0 in the presence of isoflurane. Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M. of four oocytes.