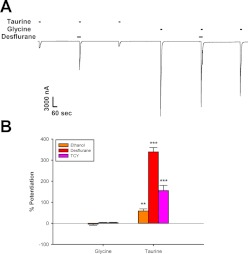
Fig. 6.
Positive allosteric modulators affect α1β-heteromeric GlyR in a similar manner to homomeric α1-GlyR. A, sample tracing demonstrating the effects of maximally effective concentrations of glycine and taurine applied with and without 1.76 mM desflurane. The tracing shows 30-s preincubations with desflurane followed immediately by 15-s applications of either 10 mM glycine or 100 mM taurine plus desflurane. Each of these applications was preceded and followed by applications of 10 mM glycine or 100 mM taurine, respectively. Horizontal bars over tracings indicate time of exposure to glycine, taurine, or desflurane. B, summary of the effects of 200 mM ethanol, 1.76 mM desflurane, or 0.39 mM TCY on 15-s applications of maximally effective concentrations of glycine or taurine. The y-axis represents the percentage change in current observed in the presence of modulator compared with that produced by glycine or taurine applied alone. Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M. of eight to nine oocytes for each modulator tested. **, P < 0.01, ***, P < 0.001 comparing glycine with taurine.