Fig. 2.
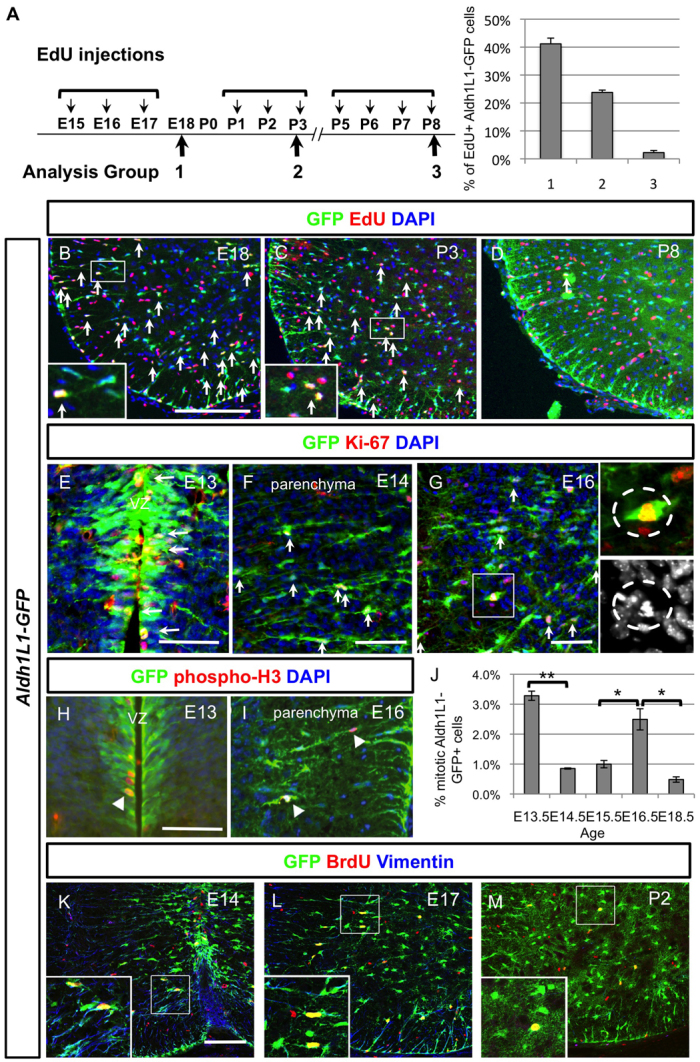
Characterisation of astrocyte proliferation at various stages of development and identification of the intermediate astrocyte progenitors (IAPs). (A) Timetable of the thymidine analogue EdU administration at three developmental time periods (E15-17, P1-3 and P5-8) and quantification of EdU+ Aldh1L1-GFP+ cells at these three stages obtained by counting spinal cord hemisections (n=3). Note that the detailed number is listed in supplementary material Table S1. (B-D) Spinal cord sections from these three different EdU tracing experiments are shown and EdU+ Aldh1L1-GFP+ are indicated with arrows. Note that the ones that were picked as positive ones are indicated in the higher power picture. (E-G) At E13 (E), Aldh1L1-GFP+ cells are proliferating at the VZ and labelled with Ki-67 in red (marked by arrows). After this, Aldh1L1-GFP+ cells migrate out from VZ and reside in the parenchyma at E14 (F) or E16 (G), some of them can be labelled with proliferation marker Ki-67 (indicated with arrows) and we have termed these cells intermediate astrocyte progenitors (IAPs). The mitotic cells can also be observed (indicated in the insets) among these IAPs. DAPI staining is used to identify the chromosomal condensation of a typical mitotic cell. (H-J) Colocalisation of mitotic marker phospho-histone 3 with Aldh1L1-GFP+ cells is observed in VZ at E13 (H) and parenchyma at E16 (I) (indicated by arrowheads). Quantification of mitotic Aldh1L1-GFP+ cells represents the average of triplicate samples from all ages except E14.5 (duplicate), with four to six sections counted per animal. Graph shows average ± s.e.m., statistics calculated using ANOVA. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (K-M) By acute BrdU labelling during the proliferative period, Aldh1L1-GFP cells express some radial characteristics (vimentin in blue) at early time points (E14 and E17) whereas fewer Aldh1L1-GFP+ cells are proliferating at postnatal stage and did not express vimentin. Scale bars: 200 μm in B; 50 μm in E-H; 100 μm in K.
