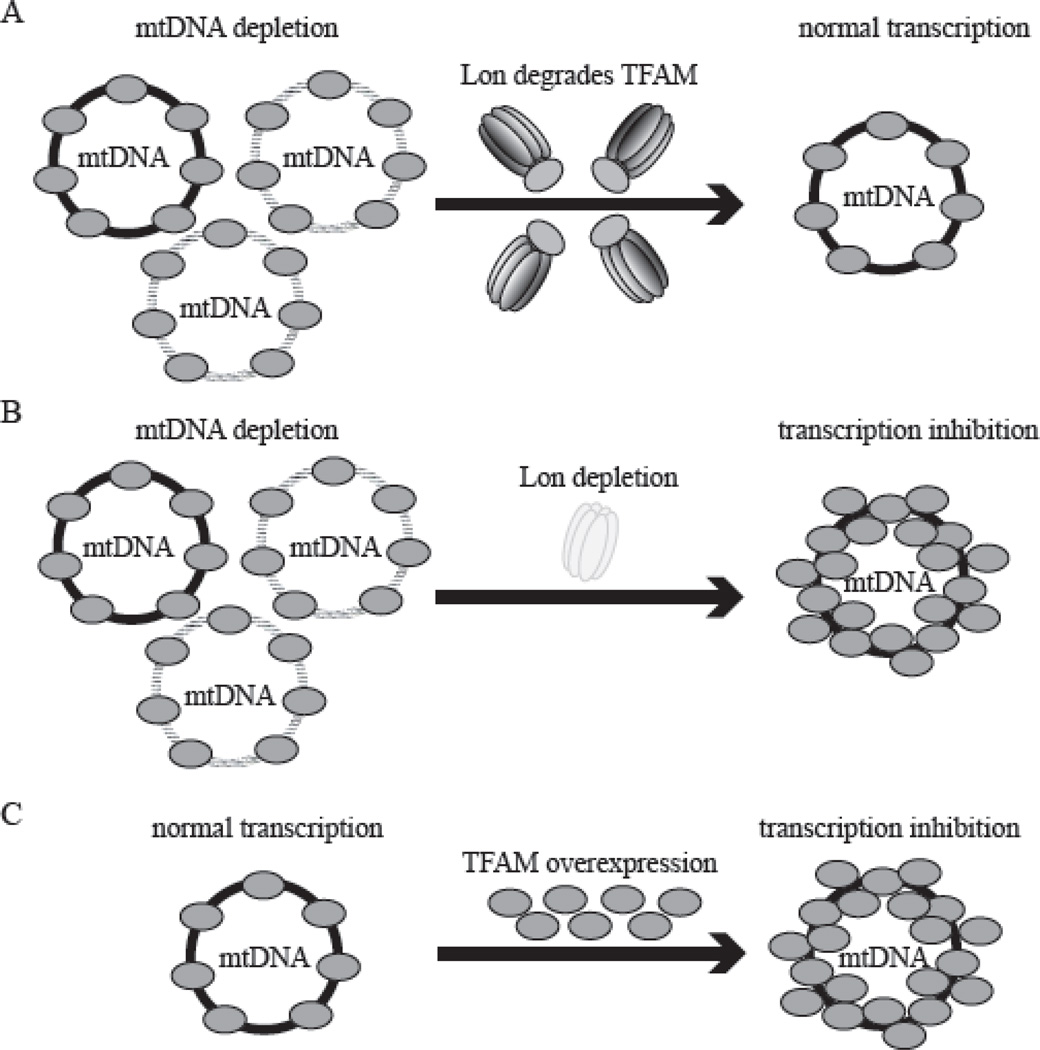
Figure 4. Lon protease degrades TFAM to stabilize the TFAM: mtDNA ratio.
A, Upon reduction of mtDNA copy number in normal cells, Lon degrades TFAM to normalize the TFAM: mtDNA ratio. As a result of this process, mtDNA transcription occurs normally. B, Upon mtDNA reduction in Lon-depleted cells, TFAM is not degraded, resulting in a dramatic increase in the TFAM: mtDNA ratio. This results in a severe inhibition in mtDNA transcription, which is likely caused by mtDNA overpackaging by TFAM. C, Excess TFAM overexpression leads to an increase in the TFAM: mtDNA ratio, resulting in a severe inhibition in mtDNA transcription.