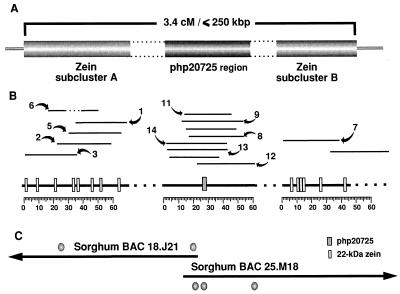
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the 22-kDa α-zein cluster region in maize and utilization of syntenic sorghum BACs in gap closure and single-copy marker identification. (A) Using a BSSS53/Mo17×Mo17 backcross, the 22-kDa zein genes clustered in chromosome 4S have been mapped as far apart as 3.4 cM (5). However, using long-range restriction analysis, we have estimated that the cluster has a maximum size of only 250 kb. The 22-kDa zein genes in the cluster are further grouped in two subclusters, approximately 60 kb apart. The RFLP marker php20725 is located in the intermediate region, between the 22-kDa zein subclusters. (B) To characterize the organization of this gene cluster, we constructed a physical map based on cosmid overlaps. The high density of the nearly identical 22-kDa zein sequences in the cluster provided useful tags for ordering contigs, but two gaps remain in regions with high density of highly repetitive DNA. Cosmid numbers correspond to those in Fig. 2. (C) Incorporation of the sorghum BACs described in Fig. 2 into the physical map of the zein cluster in maize (V.L., R. Wing, and J.M., unpublished work). Filled circles on BACs indicate sequences found to cross-hybridize in both species, corresponding to single- and low-copy elements.