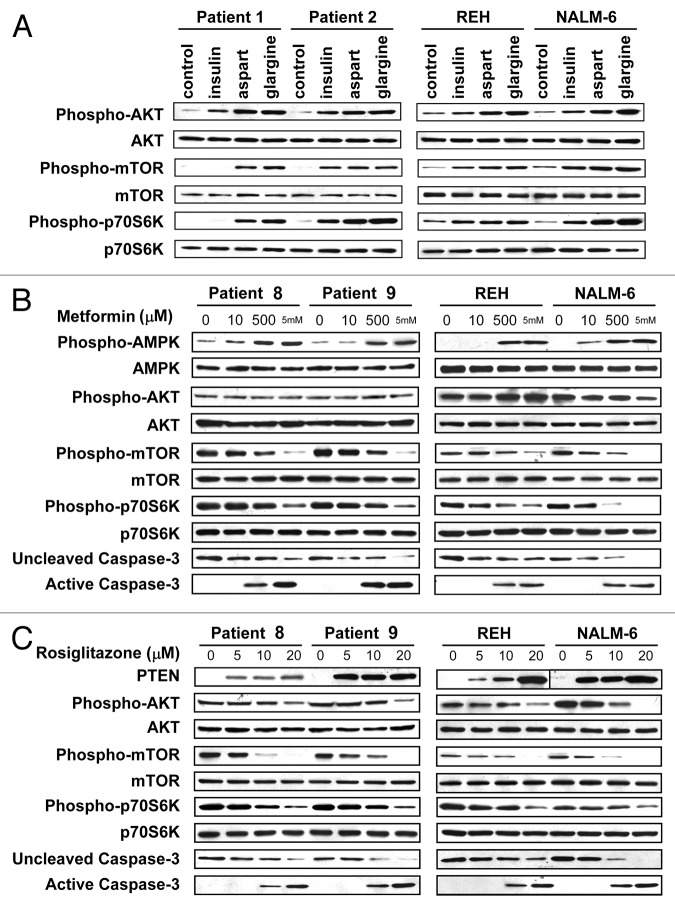
Figure 4. Differential effects of diabetes medications on AKT/mTOR signaling in leukemic cells. Immunoblots are shown with the antigens labeled to the left and the cell source and treatment labeled above. (A) 24 h treatments of human insulin, aspart and glargine at equi-hypoglycemic concentration (8 mIU/L) activated the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, and aspart and glargine activated this pathway to a higher degree than human insulin. (B) Metformin at increasing concentrations for 48 h dose-dependently increased activation of AMPK, which inhibited phosphorylation/activation of mTOR and p70S6K, and activated caspase-3 (a marker of apoptosis) while having no effect on the phosphorylation of AKT. (C) Rosiglitazone at increasing concentrations for 48 h dose-dependently increased expression of PTEN, which inhibited phosphorylation/ activation of AKT, mTOR and p70S6K, and activated caspase-3.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.