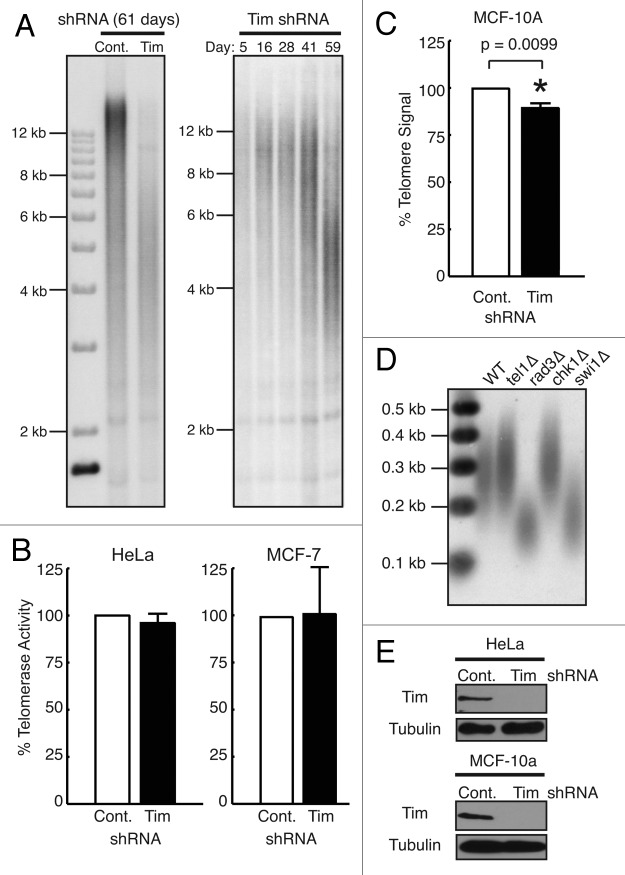
Figure 1. Timeless depletion leads to loss of telomeric DNA. (A) Telomere restriction fragment (TRF) Southern blotting analysis in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were infected by lentivirus expressing control or Timeless shRNA and continuously cultured under selection for the indicated days. Genomic DNA was prepared, digested with RsaI and HinfI, and processed for TRF Southern blot analyses using a radiolabeled telomere-specific probe. RsaI and HinfI are frequent cutters that digest genomic DNA, but do not target telomere repeats,67 generating a broad telomere hybridization signal ranging from 2 kb to 20 kb in HeLa cells. (B) Quantitative telomerase activity assay. Telomerase activity in Timeless shRNA cells is shown as a value relative to the activity in control shRNA cells. Cell line is indicated on each graph. Data are from at least three independent experiments and error bars represent standard deviations. (C) Telomere Flow-FISH assay of MCF-10A cells expressing the indicated shRNA. Six days post infection, cells were subjected to Telomere Flow-FISH using a FITC-conjugated telomere-specific probe, analyzing telomere signal in G1 cells. Error bars correspond to standard deviations obtained from three independent experiments. *The P-value determined by paired Student’s t-test is indicated. (D) Telomere restriction analysis of S. pombe cells. Genomic DNA prepared from the indicated cells was digested by ApaI and processed for Southern blot using a telomere probe. The ApaI site is located 30–40 bp away from telomeric repeat sequences of S. pombe chromosome termini,74 generating a ~300 bp telomere hybridization signal in the wild-type (WT) strain. (E) western blotting analysis of Timeless (Tim) protein in HeLa and MCF-10A cells expressing the indicated shRNA are shown, confirming knockdown of Timeless protein. Tubulin was used as a loading control.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.