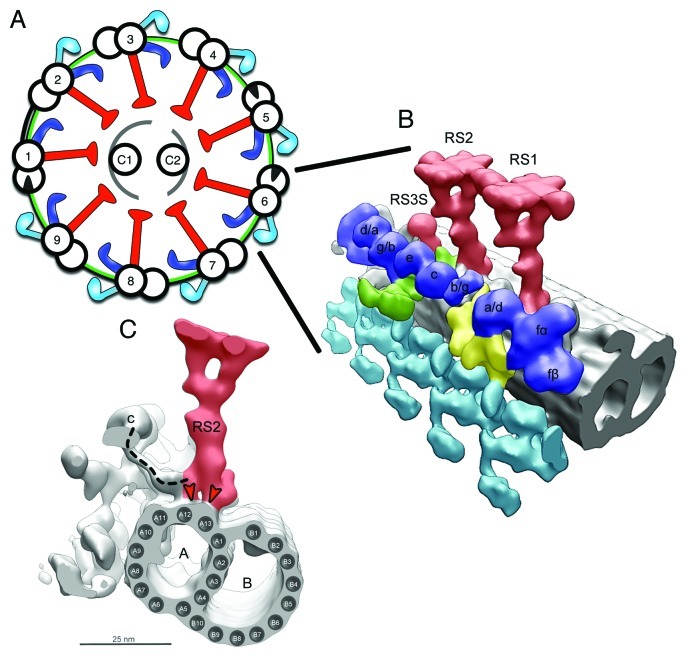
Figure 1. Placement of the RSs in the Axoneme. (A) Scheme of the 9 + 2 axonemal structure, showing the placement of main axonemal components. Radial spokes (red), inner dynein arms (blue), outer dynein arms (turquoise), microtubules (black), N‐DRC (green), central pair complex (gray). (B) Surface renderings of tomographic reconstruction of a 96 nm repeat along one of the MTDs of Chlamydomonas. The microtubules are shown in gray, the rest of the color‐coding is according to (A). RS1, RS2, and RS3 stump (RS3S) are shown. Isoforms of inner arm dyneins are indicated. Dynein b/g is either dynein b or dynein g, but it has not been determined which of the two this dynein is. It is the same case for dynein g/b, a/d, d/a. (C) Side view seen from the proximal end showing RS2, IDA c, ODA, and the microtubule doublet. A, A‐microtubule; B, B‐microtubule. The dashed line indicates the dynein c tail connecting to the RS2 base. The red arrowheads show the binding of the bifurcated base of RS to the protofilaments A12 and A13 of the A‐microtubule. [(B) was modified from ©Pigino et al., 2011. Originally published in JCB. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201106125].

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.