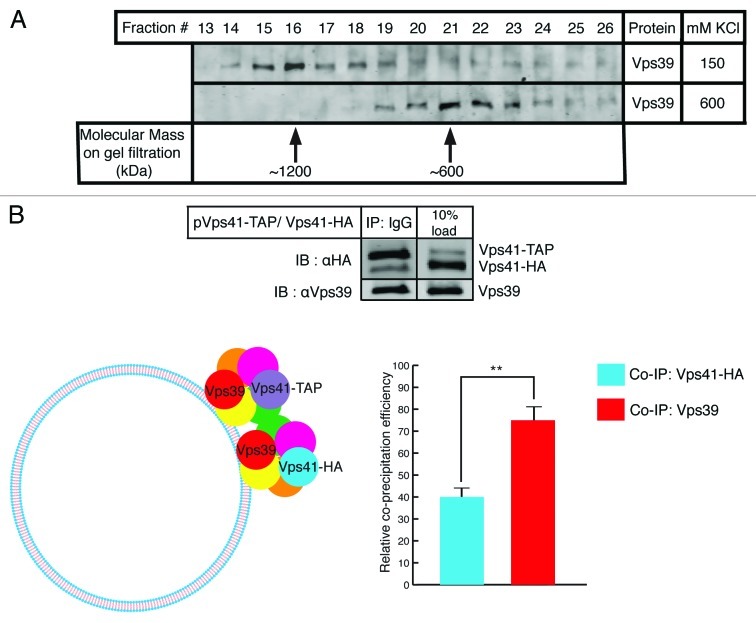
Figure 1. HOPS is a dimeric complex on the surface of yeast vacuoles. (A) Gel filtration analysis of purified yeast vacuoles. Fractions 13–26 from Superose 6 gel filtration of solubilized vacuoles were inspected using SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting against Vps39. When vacuoles were processed at 150 mM KCl in the solubilization buffer, HOPS predominantly runs in fraction 16 (top lane). At 600 mM KCl, HOPS predominantly runs in fraction 21 (bottom lane). Arrows indicate molecular weights. (B) Cis-HOPS complexes assayed by differently tagged Vps41. Vacuoles from the Vps41-HA strain harboring a Vps41-TAP plasmid were processed as described in Materials and Methods. After IgG pull down of Vps41-TAP, co-precipitating proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting. In the top panel, the left lane shows precipitated Vps41-TAP, co-precipitating Vps41-HA and Vps39 and the right lane displays corresponding protein inputs. The bottom panel depicts relative co-precipitation efficiencies of Vps41-HA and Vps39 quantified by Odyssey densitometry and normalized from three independent experiments. Vps39 is consistently found to co-precipitate at approximately twice the efficiency of that of Vps41-HA (p < 0.01).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.