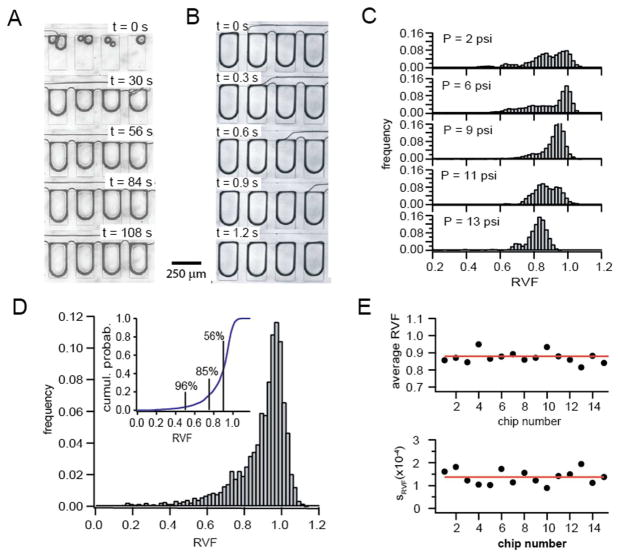
Fig. 2.
Sample self-digitization in the dLAMP SD chip. (A) Sequential images showing the initial filling of the side-chamber array with aqueous solution. After priming the chip with oil, the aqueous sample entered the main channel and distributed itself into the side compartments, displacing the oil phase in the chambers. (B) Sequence of images showing the self-digitization of aqueous sample in the side chambers. After the whole aqueous phase entered the chip, the tailing oil phase in the main channel isolated individual nanoliter sized droplets in the side chambers. (C) Dependence of the distribution of droplet size in the side chambers on applied pressure. The most uniform distribution with the highest average relative volume fraction (RVF) was obtained for an external pressure of 7 psi. Lower and higher pressures resulted in formation of droplets with more variable volumes and reduced RVF. (D) Size distribution of RVF values for 5000 self-digitized droplets from 16 individual chips. The external pressure was set to 7 psi in all experiments. The average RVF of all droplets was 0.89 ± 0.14. The inset shows the cumulative distribution of RVF values. The numbers correspond to the fraction of droplets with an RVF exceeding 50%, 75% and 90%, respectively. For example, 85% of all droplets filled out more than 75% of the chamber. (E) Reproducibility of sample self- digitization. Shown are the average RVF value and the standard deviation for 15 individual chips, each filled with 7-psi external pressure.