Figure 3.
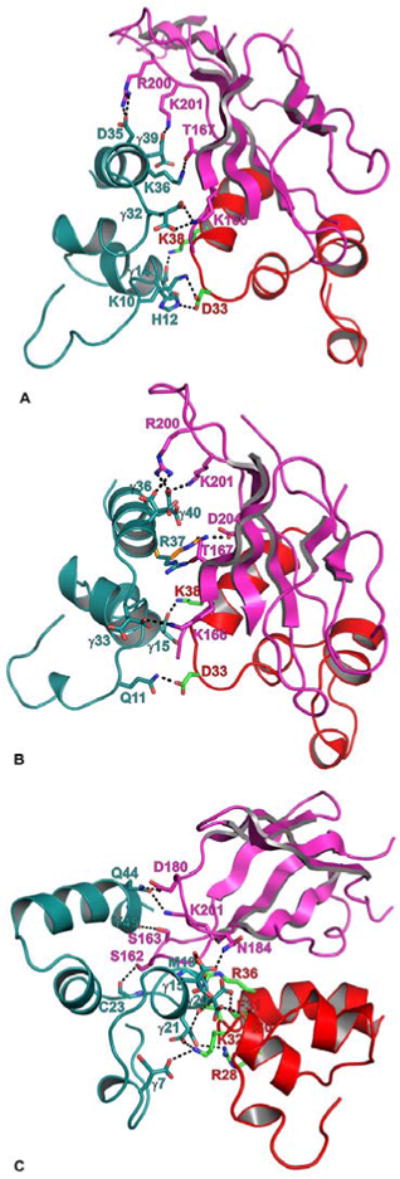
Modeled interactions of FVIIa/sTF with the Gla domains of FXa, FIXaand FIXalpha. The interacting residues of FVIIa-Gla (red), sTF (magenta) and FXa-Gla (deep teal) are shown in stick representation. The carbon atoms are green in FVIIa-Gla, magenta in sTF, and deep teal in the Gla domains of FXa, FIXa and FIXalpha. The N and O atoms are blue and red, respectively. The hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines. A) The modeled interaction of FXa-Gla with sTF and FVIIa-Gla. FXa-Gla:sTF—Gla32:K166, D35:R200, Gla39:K201 and K36:T167; FXa-Gla:FVIIa-Gla—K10:D33, H12:D33 and Gla14:K38. B) The modeled interaction of FIXa-Gla with sTF and FVIIa-Gla. FIXa-Gla:sTF—Gla33:K166, Gla36:R200, R37:D204/T167, and Gla40:R200/K201; FIXa-Gla:VIIa-Gla—Q11:D33 and Gla15:K38. C) The modeled interaction of FIXalpha-Gla with sTF and FVIIa-Gla. FIXalpha-Gla:sTF—Gla15:N184, C23:S162, Q44:D180/201 and Y45:S163; FIXalpha-Gla:FVIIa-Gla—Gla7:K32; M19:R36, Gla20:F31/I30 and Gla21:R28/K32.
