Fig. 1.
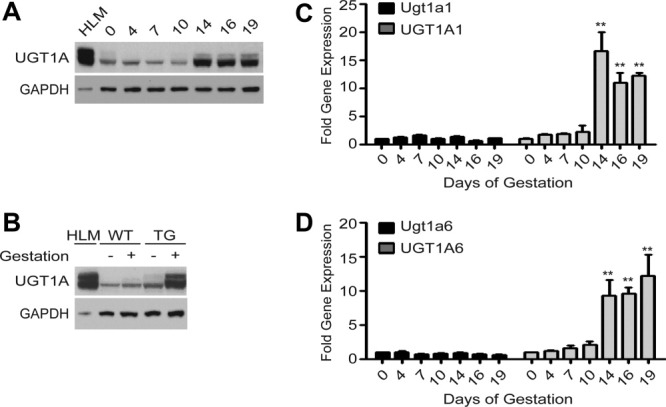
Induction of the UGT1 locus in TgUGT1 mice. Age-matched female TgUGT1 mice were mated with wildtype mice. The following morning, female mice with the presence of a vaginal plug were removed, housed separately, and timed as gestation day 1. Pregnant mice were sacrificed at gestation days (GD) 4, 7, 10, 14, 16, and 19. Samples from at least three nonpregnant female TgUGT1 mice were used as controls. Liver microsomes and RNA from the nonpregnant control and pregnant mice were prepared. (A) Immunoblot detection of UGT1A proteins. Liver microsomes prepared from pregnant TgUGT1 mice at progressive stages of pregnancy were analyzed on 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and the UGT1A proteins detected on immunoblots by using an anti-UGT1A antibody and anti-GAPDH antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Human liver microsomes (HLM) were used as a positive control. (B) Immunoblot of UGT1A proteins from liver microsomes prepared from female wildtype and TgUGT1 mice that were pregnant for 16 days. Control samples were prepared from nonpregnant wildtype and TgUGT1 mice. (C) Total RNA was isolated from liver samples taken from the pregnant TgUGT1 mice and used in RT and Q-PCR analysis to examine murine UGT1A1 RNA (Ugt1a1) expression and human UGT1A1 RNA expression. Student's t test was used to evaluate the statistical significance (**P < 0.01). (D) The same RNA samples were used to quantitate murine Ugt1a6 and human UGT1A6 gene expression (**P < 0.01, t test).
