Figure 2.
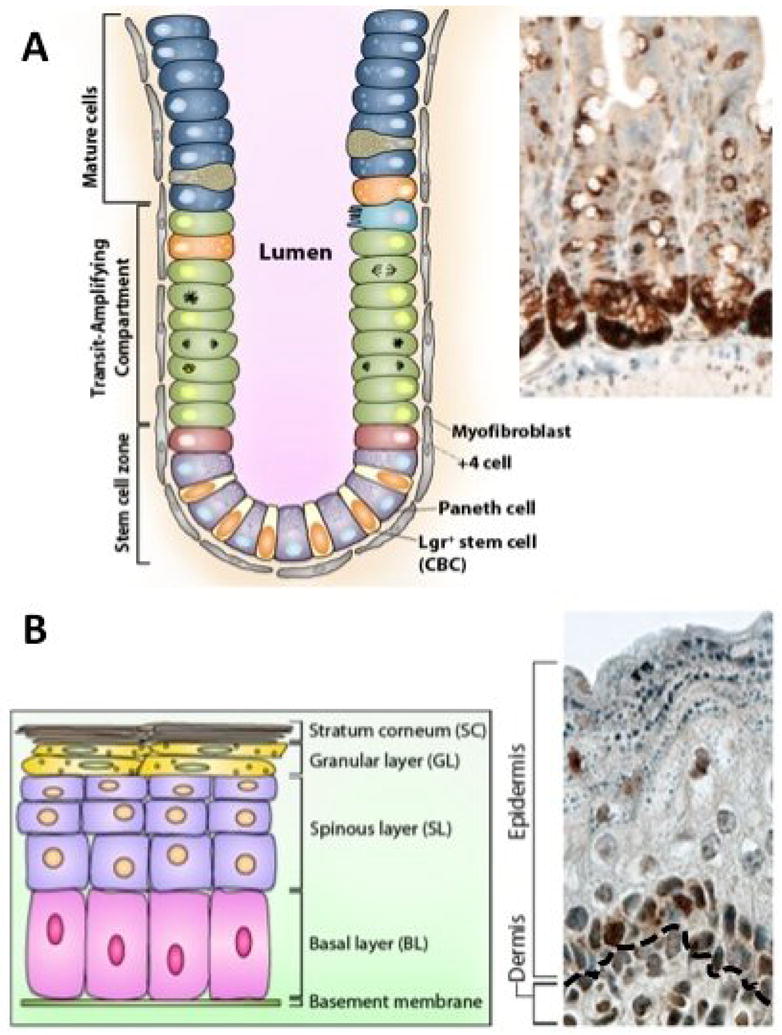
YAP expression in stem/progenitor cell compartments. (A) Intestinal crypt architecture with quiescent (+4) and active crypt base columnar (CBC, Lgr5+) stem cells shown. Also shown but not discussed in the text are mature cell types, the transit-amplifying compartment, and components of the intestinal stroma (myofibroblasts). Inset depicts YAP localization in crypts, in wildtype intestine. (B) Epidermal architecture with progenitor cells residing in the basal layer (BL). Asymmetric divisions in this compartment produces short-lived progenitor cells that stratify as they differentiate, leaving the basal layer and moving up into the spinous layer (SL), granular layer (GL), and stratum corneum (SC). Inset depicts significant YAP localization in the basal layer of wildtype skin. Black dotted line represents the border between the dermis and epidermis.
