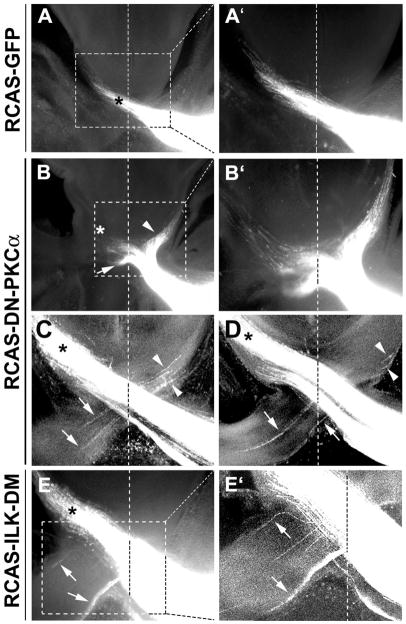
Figure 6.
Expression of DN-PKCα or ILK-DM resulted in misguidance of chick RGC axons at the optic chiasm. The optic vesicles of the chick embryos were injected with RCAS viruses at E1.5 and DiI was injected into the eye cups of the right eyes at E7. DiI was allowed to diffuse for 2 to 3 weeks to label the RGC axon pathway. A, In RCAS-GFP infected retinas, DiI-labeled RGC axons exhibited normal pathfinding at the chiasm projecting into the contralateral optic tract (asterisk). B–E′, Misprojection of RGC axons was found at the chiasm in the samples infected with RCAS-DN-PKCα (B–D) or RCAS-ILK-DM (E, E′). Axons were misrouted into the ipsilateral optic tract (arrowheads) and contralateral optic nerve (arrows). A′, B′, E′ are higher magnification views of the regions boxed in A, B, E, respectively. C, D, Confocal images of two consecutive sections of a RCAS-DN-PKCα infected sample. Vertical dash line indicates the midline. * indicates the contralateral optic tract.