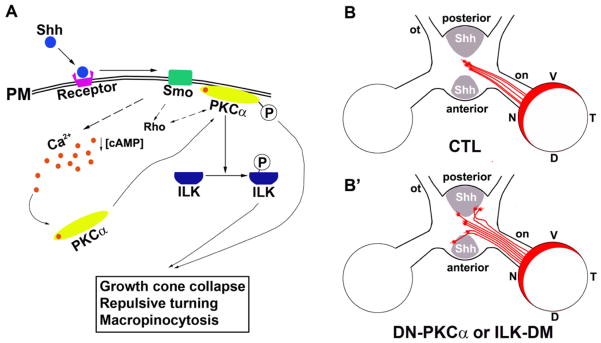
Figure 8.
A model of PKCα-ILK signaling in the RGC axon guidance. A, In chick RGC axons, Shh decreases [cAMP]I (Trousse et al., 2001) and increases [Ca2+]i leading to phosphorylation and translocation of PKCα to the plasma membrane. Activated PKCαphosphorylates ILK. The PKCα-ILK and the Rho GTPase pathways (Kolpak et al., 2009) are critical for Shh-induced negative axon guidance effects. B, In wild-type chick embryos, RGC axons that originate from optic disc cross at the optic chiasm to the contralateral optic tract. B′, Expression of DN-PKCα or ILK-DM results in a portion of axons that fail to respond to Shh, leading to aberrant axon pathfinding at the chiasm. PM, plasma membrane; V, Ventral; D, dorsal; N, nasal; T, temporal; on, optic nerve; ot, optic tract.